CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Sources of energy which are known to most of the people. E.g., fossil fuels, biomass etc.
Non-conventional Sources of Energy
Fossil fuels are the remains of prehistoric plants and animals which got buried deep inside the early millions of years ago due to some natural processes.
The energy of fossil fuels is in fact, that solar energy which was trapped by natural processes a very long time ago. Coal, petroleum and natural gas are fossil fuels.
Formation of Fossil Fuels: During its formation, an entire organism or its parts often get buried in sand or mud. These, then decay and disintegrate leaving no signs of their existence. In fact, the harder parts of organisms after their death, settle down and are covered by sediments and subjected to extreme pressure and temperature of the earth converts them into fossil fuels, the process is referred to as fossilization.
Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels:
Hydropower plants convert the potential energy of falling water into electricity.
In order to produce hydel electricity, high-rise dams are constructed on the river to obstruct the flow of water and thereby collect water in larger reservoirs.
The water level rises and in this process, the kinetic energy of flowing water gets transformed into potential energy.
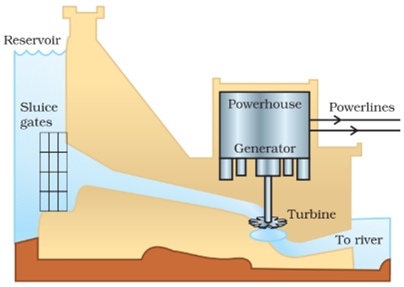
Advantages of generating hydroelectricity:
Disadvantages :
The dead parts of plants and trees and the waste materials of animals and man are called Biomass.
The biomass includes
Biogas: Biogas is a mixture of gases produced by anaerobic degradation of biomass in the presence of water but in the absence of oxygen. It is a renewable source of energy on account of its production from vastly and continuously available organic wastes.
The composition of Biogas: Biogas is mainly composed methane (up to 75%), CO2 (25%) and traces of other gases such as nitrogen and hydrogen. Whereas methane is a high-value calorific fuel, carbon dioxide is an inert gas.
Biogas is prepared in biogas plants which are of two types:
Advantages of Biogas:
The dead parts of plants and trees and the waste materials of animals and man are called Biomass.
The biomass includes
Biogas: Biogas is a mixture of gases produced by anaerobic degradation of biomass in the presence of water but in the absence of oxygen. It is a renewable source of energy on account of its production from vastly and continuously available organic wastes.
The composition of Biogas: Biogas is mainly composed methane (up to 75%), CO2 (25%) and traces of other gases such as nitrogen and hydrogen. Whereas methane is a high-value calorific fuel, carbon dioxide is an inert gas.
Biogas is prepared in biogas plants which are of two types:
Advantages of Biogas:
Wind Energy: When large masses of air move from one place to another it is referred to as wind. During this process, kinetic energy gets associated with it which is referred to as wind energy.
Principle of utilisation of wind energy:
Wind energy is efficiently converted into electrical energy with the aid of a windmill. A windmill is a large fan having big blades, which rotate by the force exerted by moving wind on them. These blades remain continuously rotating as long as the wind is blowing and can be used to drive a large number of machines like water pumps, flour mills etc. But these days a windmill is used to generate an electric current which is used for various purposes and therefore wind power stations are established all over the world which convert wind energy directly into electrical energy.
Uses of wind energy: -
Advantages of generating wind energy:
Denmark is called the ‘Country of Winds’.
India is ranked 5th in harnessing wind energy for the production of electricity.
In India largest wind energy farm has been established near Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu and it generates 380 MW of electricity.
The term thermal power plant is used since fuel is burnt to produce heat energy which is converted into electrical energy.
A large amount of fossil fuels are burnt every day in power stations to heat up water to produce steam which further runs the turbine to generate electricity. The transmission of electricity is more efficient than transporting coal or petroleum over the same distance. Therefore, many thermal power plants are set up near coal or oil fields.