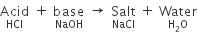CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
ACIDS:
Strong Acids: HCl, H2SO4, HNO3
Weak Acids: CH3COOH, Oxalic acid, Lactic acid
Concentrated Acid: Having more amount of acid + less amount of water
Dilute Acid: Having more amount of water + less amount of acid
BASES :
Strong Bases: NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2
Weak Bases: NH4OH
Alkalis: These are bases which are soluble in water [NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2].
SALTS:
Salts: - A salt is a compound which is formed by the neutralization reaction between an acid and base.
For example, sodium chloride is formed by reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.