CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
The rules of heredity determine the process by which the traits and the characteristics are relatively inherited. In other words, the transmission of characters/traits from one generation to the next generation.
The inheritable characteristics may be morphological/anatomical/physiological/reproductive and are also known as traits.
Genotype: The complete set of genes in an organism’s genome is called genotype.
Phenotype: The observable characters in an organism make the phenotype. The phenotype is a result of genotype’s interaction with the environment. Due to this reason, many phenotypes are not inheritable.
Acquired Traits: Traits; which are acquired due to interaction with the environment; are called acquired traits. Acquired traits are not inheritable.
Inheritable Traits: Traits; which can be expressed in subsequent generations; are called inheritable traits. Such traits bring a change in the genotype of the organism and hence become inheritable.
Dihybrid Cross: A cross macle between two plants having two pairs of contrasting characters is called dihybrid cross.
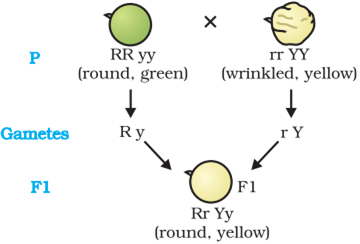
When plants of F1 generation were allowed to self-pollinate.

PHENOTYPIC RATIO :
Round, yellow: 9
Round, green : 3
Wrinkled, yellow : 3
Wrinkled, green : 1
GENOTYPIC RATIO :
RRYY: 1
RRYy: 2
RrYY: 2
RRyy: 1
RrYy: 4
Rryy: 2
rrYY: 1
rrYy: 2
rryy: 1
RATIO: 1:2:2:1:4:2:1:2:1
Observations :
1. When RRYY was crossed with rryy in F generation all 1 were Rr Yy round and yellow seeds.
2. Self-pollination of F plants gave parental phenotype + two 1 mixtures (recombinants) Round wrinkled,
green yellow :seeds plants appeared in the ratio of 9:3:3:1
Conclusions :
1. Round and yellow seeds are DOMINANTcharacters
2. The occurrence of new phenotypic combinations shows that genes for round and yellow seeds are inherited independently of each other.
A child bears all the basic features of a human being. However, it does not look exactly like its parents, and human populations show a great deal of variation.
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822-1884) worked out the first ever scientific experimental study on heredity.
Mendel started studying inheritance in peas. He performed series of experiments with pea plants for 7 long years (1856- 1863). He kept proper count of individuals exhibiting a particular trait in each generation. Mendel, with his experiments, found out the principles based on which it could guess how characters get inherited or passed to the offspring. Many rules of heredity were established often termed as “LAWS OF MENDELIAN INHERITANCE”.
Mendel is known as the ‘Father of Genetics’ due to his significant contribution to establishing the basic principles in Genetics.
Mendel crossed a tall plant with a dwarf plant, produced progeny and calculated the percentage of tallness and dwarfness in subsequent generations. When a pure breeding tall plant was crossed with a pure-breeding dwarf plant, all plants were tall in the first filial generation (F1) i.e., there was not any medium height plants or dwarf plants.
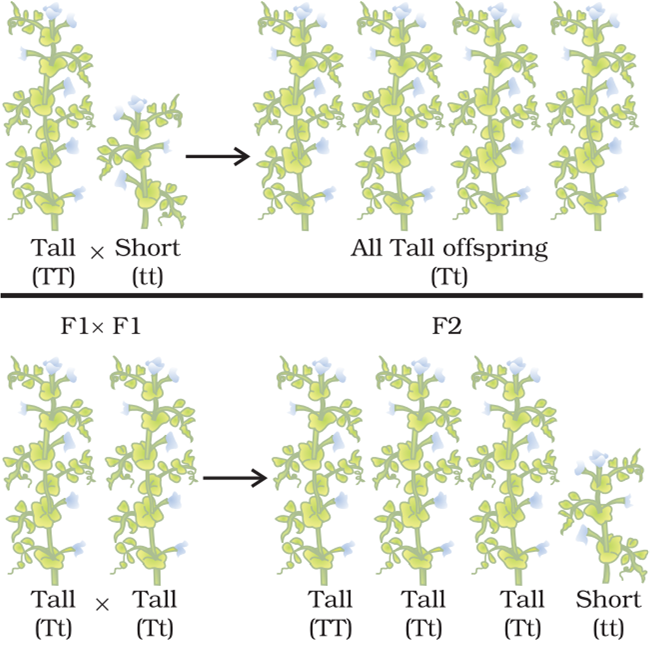
This means that only one of the parental traits were seen and not the mixture of the two. When such an F1 tall plant was allowed to have self-pollination, both the tall and dwarf plants appeared in second filial generation (F2). in the ratio of 3:1. This indicates that both tallness and dwarfness were inherited in the F1 plants but only tallness trait was expressed.
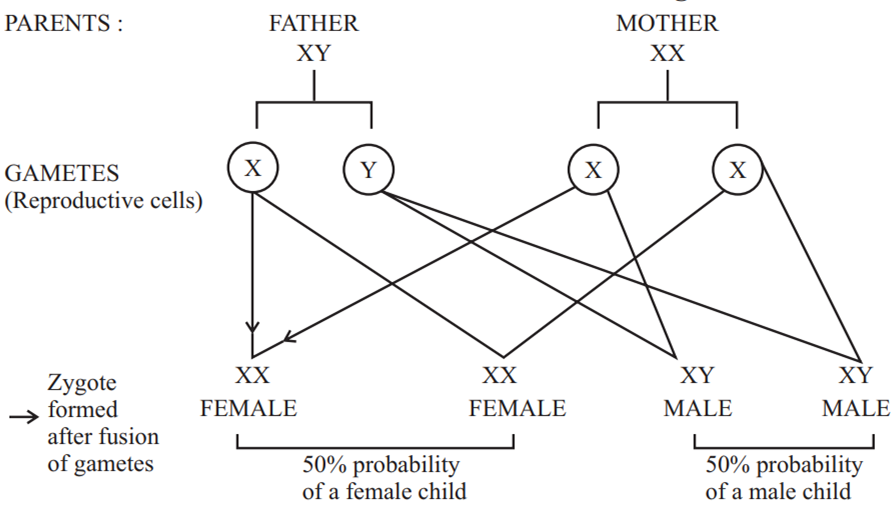
Somatic cells in human beings contain 23 pairs of chromosomes. Out of them, the 23rd pair is composed of different types of chromosomes which are named as X and Y chromosomes.
The 23rd pair contains one X and one Y chromosome in a male. On the other hand, the 23rd pair in a female contains X chromosomes.
This means that all the eggs would have X chromosome as the 23rd chromosome, while a sperm may have either X or Y chromosome as the 23rd chromosome.
When a sperm with X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the resulting zygote would develop into a female child.
When a sperm with Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the resulting zygote would develop into a male child.