CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
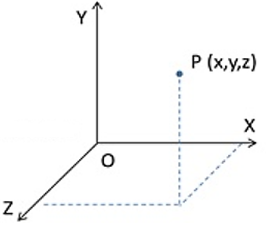
Position can be specified through reference point and a set of axes.
In the figure, the point O is a reference point and the three axes i.e., x, y and z are known as coordinates system.
The coordinates system along with a time is known as a frame of reference.
if a body changes its position as time passes with respect to the frame of reference, it is said to be in motion.
For example, A passenger standing on bus stand observes that shop store on a bus stand is at rest. But when the same passenger is passing away in a bus through bus stand, observes that shop store is in motion. In both conditions the observer is right.
But observations are different because in first situation observer stands on a bus stand, which is reference frame at rest and in second situation observer moving in the bus, which is reference frame in motion.
So rest and motion are relative terms. It depends upon the frame of references.
Shortest Distance between two points is known as a displacement.
Let x1 and x2 be the positions of an object at time t1 and t2. Then its displacement, denoted by ∆x, in
time ∆t = (t2- t1), is given by the difference between the final and initial positions :
∆x = x2– x1
(We use the Greek letter delta (∆) to denote a change in a quantity.)
If x2> x1, ∆x is positive; and if x2< x1, ∆x is negative.
Displacement has both magnitude and direction which is also known as a vector quantity.
Dimension : [M0L1T0]
Unit: metre (S.I.)
The magnitude of displacement may or may not be equal to the path length traversed by an object.
The magnitude of the displacement for a course of motion may be zero but the corresponding path length is not zero.
For example, for the motion of the car from O to P, the path length is +360 m and the displacement is +360 m. In this case, the magnitude of displacement (360 m) is equal to the path length (360 m). But consider the motion of the car from O to P and back to Q. In this case, the path length = (+360 m) + (+120 m) = +480 m. However, the displacement = (+240 m) –(0 m) = + 240 m. Thus, the magnitude of displacement (240 m) is not equal to the path length (480 m).

The motion of a body in a straight line is called a one-dimensional motion or straight line motion.
Here one coordinate of the position of a body changes with time.
Consider the motion of a car along a straight line.
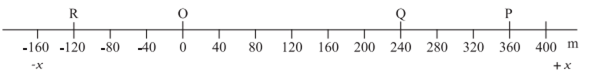
Take two cases of motion. In the first case, the car moves from O to P. Then the distance moved by car is OP = +360 m.
In the second case, the car move from P to Q. = +120 m.
This distance is called the path length travelled by car.
Path length is a scalar quantity — a quantity that has a magnitude only and no direction.
Dimension formula - [M0L1T0]
S.I unit - meter