CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Total Internal Reflection
When light enters obliquely from a denser medium to a rarer medium and the angle of incidence exceeds critical angle, the light reflects in the denser medium. This is called internal reflection.
Conditions necessary for Internal Reflection
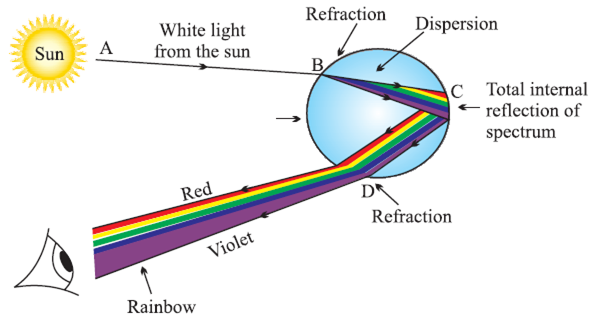
Rainbow
Some water droplets remain suspended in air after the rain. These droplets behave as a glass prism. When light enters the raindrop, it first refracts and disperses. Then it reflects internally and again refracts as it comes out of the drop and the seven colours reach the eye of the observer in form of a rainbow.
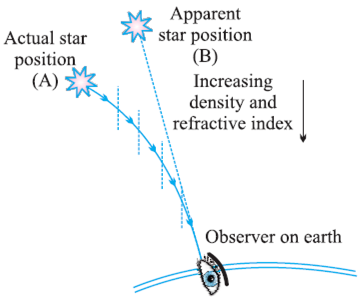
Atmospheric Refraction: The refraction by different layers of the atmosphere is called atmospheric refraction.
The sun appears about two minutes earlier than actual sunrise and the sun remains visible for about two minutes after actual sunset.
When the sun is below the horizon, the rays have to pass from rarer to denser medium. So rays bend towards the normal. As a result, the sun appears higher than its actual position.

