 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain the process of secondary growth in the stems of woody angiosperms with the help of schematic diagrams. What is its significance?


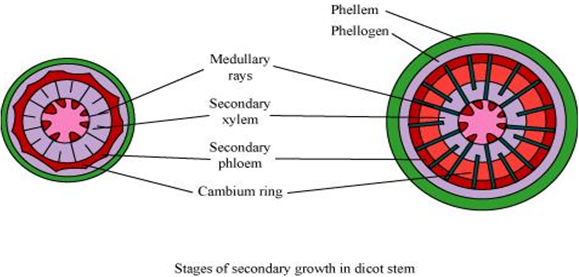
The secondary growth in plants:
i. Increases the girth of plants,
ii. Increases the amount of water and nutrients to support the growing number of leaves.
iii. Provides support to plants.
Draw illustrations to bring out anatomical difference between:
(a) Monocot root and dicot root
(b) Monocot stem and dicot stem
Cut a transverse section of young stem of a plant from your school garden and observe it under the microscope. How would you ascertain whether it is a monocot stem or a dicot stem? Give reasons.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe transverse section of a plant material shows the following anatomical features:
(a) the vascular bundles are conjoint, scattered and surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle sheaths.
(b) phloem parenchyma is absent. What will you identify it as?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeName the three basic tissue systems in the flowering plants. Give the tissue names under each system.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type