 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDescribe the internal structure of a dorsiventral leaf with the help of labelled diagrams.
Dorsiventral leaves are found in dicots. The vertical section of a dorsiventral leaf contains three distinct parts.
(i) Epiderms: Epiderms is present on both the upper surface (adaxial epiderms) and the lower surface (abaxial epiderms).
(ii) Mesophyll: Mesophyll is a tissue of the leaf present between the adaxial and abaxial epidermises. It is differentiated into the palisade parenchyma (composed of tall, compactly-placed cells) and the spongy parenchyma (comprising oval or round, loosely-arranged cells with inter cellular spaces). Mesophyll contains the chloroplasts which perform the function of photosynthesis.
(iii) Vascular system: The vascular bundles present in leaves are conjoint and closed. They are surrounded by thick layers of bundle-sheath cells.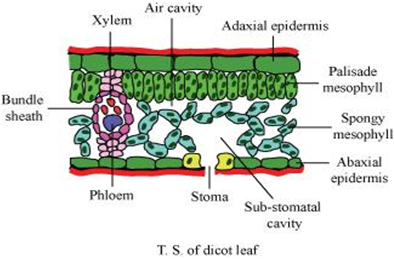
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeCork cambium forms tissues that form the cork. Do you agree with this statement? Explain.
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA transverse section of stem is stained first with safranin and then with fast green following the usual schedule of double staining for the preparation of a permanent slide. What would be the colour of the stained xylem and phloem?
Red and green
Green and Red
Orange and yellow
Purple and Orange
Cells of this tissue are living and show angular wall thickening. They also provide mechanical support. The tissue is
Xylem
Sclerenchyma
Collenchyma
Epidermis
A conjoint and open vascular bundle will be observed in the transverse section of
Monocot root
Monocot stem
Dicot root
Dicot stem
Match the followings and choose the correct option from below
A. Meristem i. Photosynthesis, storage
B. Parenchyma ii. mechanical support
C. Collenchyma iii. Actively dividing cells
D. Sclerenchyma iv. stomata
E. Epidermal tissue v. sclereids
Options:
a. A-i, B-iii, C-v, D-ii, E-iv
b. A-iii, B-i, C-ii, D-v, E-iv
c. A-ii, B-iv, C-v, D-i, E-iii
d. A-v, B-iv, C-iii, D-ii, E-i
Match the following and choose the correct option from below
A. Cuticle i. guard cells
B. Bulli form cells ii. single layer
C. Stomata iii. waxy layer
D. Epidermis iv. empty colourless cell
Options:
A-iii, B-iv, C-i, D-ii
A-i, B-ii, C-iii, D-iv
A-iii, B-ii, C-iv, D-i
A-iii, B-ii, C-i, D-iv
Interfascicular cambium and cork cambium are formed due to
Cell division
Cell differentiation
Cell dedifferentiation
Redifferentiation
