 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich of the following is not correctly matched for the organism and its cell wall degrading enzyme?
Bacteria - Lysozyme
Plant cells - Cellulase
Algae - Methylase
Fungi - Chitinase
The Golgi complex plays a major role
in trapping the light and transforming it into chemical energy
in digesting proteins and carbohydrates
as energy transferring organelles
in post translational modification of proteins and glycosidation of lipids
Which one of the following organelle in the figure correctly matches with its function?
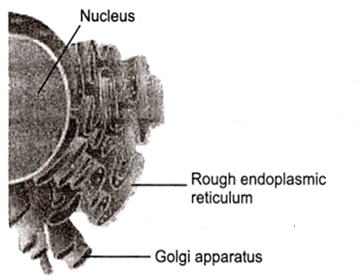
Rough endoplasmic reticulum, formation of glycoproteins
Golgi apparatus, protein synthesis
Golgi apparatus, formation of glycolipids
Rough endoplasmic reticulum, protein synthesis
Which of the following is always absent in prokaryotic cells?
Ribosome
Mitochondria
DNA
Cell wall
Objects less than 0.2 m in size cannot be see an under light microscope because
the wave length of visible light is 3900- 7800 Å
only two types of lenses are used
maximum magnifying power of ocular lens is 20 X
maximum magnifying power of objective lens is 100 X
The apoplast is located
outside the plasma membrane
in the entire cytosol
on both sides of plasma membrane
in the plastidial content
ATP synthesis in cell requires
H+ gradient across the membrane
K+ gradient across the membrane
PO4 3- gradient across the membrane
Ca2+ gradient across the membrane
A.
H+ gradient across the membrane
ATP synthesis takes place by the process of chemiosmosis, where ATP is generated via a proton (H+) gradient across the membrane.
Actions of the proton pump is the driving force of ATP. The proton pump pumps H+ ions across the membrane. It establishes a chemical gradient; the protons are high in the intermembrane space than in the matrix. Pumping of the H+ ions across the membrane makes the intermembrane space more positively charged as compared to the matrix. Hence, this is strong electrochemical gradient which energizes the ATP synthase protein to form ATP.
The eukaryotic cells have all of the followings except
peptidoglycan in the cell wall
the 80 S ribosome
nuclear membrane
mitochondria
