 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe rate of formation of new organic matter by rabbit in a grassland is called
net productivity
secondary productivity
net primary productivity
net primary productivity
Given below is a simplified model of phosphorus cycling in a terrestrial ecosystem with four blanks (A-D). Identify the blanks.
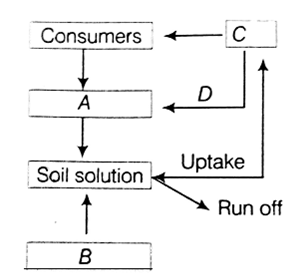
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Rock Minerals |
Detritus |
Litter fall |
Producers |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Litter fall |
Producers | Rock minerals |
Detritus |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Detritus |
Rock minerals | Producer |
Litter fall
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Detritus |
Rock minerals | Producer |
Litter fall
|
Given below is the representation of the extent of global diversity of invertebrates. What groups the four portions (A - D) represent respectively?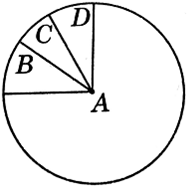
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Insects |
Crustaceans |
other animal group |
Molluscs
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Crustacean |
Insects | Molluscs | other animal groups |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Molluscs |
Other animal groups | Crustaceans | Insects |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Molluscs |
Other animal groups | Crustaceans | Insects |
If 20 J of energy is trapped at the producer level, then how much energy will be available to peacock as food in the following chain?
Plant--> Mice --> Snake --> Peacock
0.02 J
0.002 J
0.2 J
0.2 J
A.
0.02 J
According to 10% law of energy flow by Raynold Lindman. The total amount of energy that can be transferred to the next trophic level is the 10% hence, the peacock will receive 0.02 J of energy as a top consumer. Energy received by other organisms are
Plant --> 20 J
Mice --> 20 x 10 % = 2J
Snake--> 2 x 10 % = 0.2 J.
Identify the likely organisms (a), (b) (c) and (d) in the food web shown below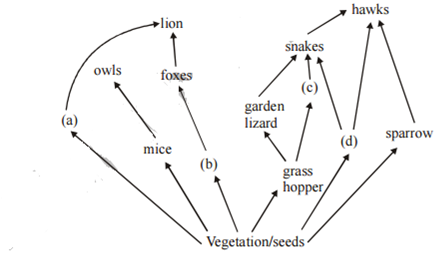
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) |
| deer | rabbit | frog | rat |
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) |
| dog | squirrel | bat | deer |
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) |
| rat | dog | tortoise | crow |
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) |
| rat | dog | tortoise | crow |
Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in a biotic community is known as
divergence
stratification
zonation
zonation
Secondary succession takes place on/in
bara rock
degraded forest
newly created pond
newly created pond
The mass of living material at a tropic level at a particular time is called
gross primary productivity
standing state
net primary productivity
net primary productivity
In an ecosystem the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis is termed as
net primary productivity
gross primary productivity
secondary productivity
secondary productivity
