 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) Why are the fruit juices bought from market clearer as compared to those made at home?
(b) Name the bioactive molecules produced by Trichoderma polysporum and Monascus purpureus.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDescribe the asexual and sexual phases of life cycle of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans.
Asexual and sexual phases of life cycle of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans.
Plasmodium requires two hosts to complete its life cycle.
ii. When female Anopheles mosquito bites a healthy human being, it releases Plasmodium, which lives in its body as sporozoite (infectious form).
iii. The parasites multiply (asexual reproduction) in the liver cells and finally burst the liver cells. Sporozoites are released in blood.
iv. Parasites enter RBCs and further multiply (asexual reproduction) here and finally burst RBCs also.
v. Bursting of RBCs is accompanied by release of a toxic substance called haemozoin (associated with fever and chills).
vi. In the RBCs, only sporozoites change into gametocytes (sexual stage). Gametocytes multiply.
vii When the diseased person is bitten by a female Anopheles mosquito, gametocytes are introduced into the mosquito.
vii Gametocytes fertilise and develop inside the intestine of mosquito to form sporozoites.
ix. Sporozoites are stored in the salivary glands of mosquito and are released into the healthy person who is bitten by this mosquito.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) Highlight the role of thymus as a lymphoid organ.
(b) Name the cells that are released from the above-mentioned gland. Mention how they help in immunity.Name of parasite the causes filariasis in humans. Mention its two diagnostic symptoms. How is this transmitted to others?
Study a part of the life cycle of malarial parasite given below. Answer the questions that follow: 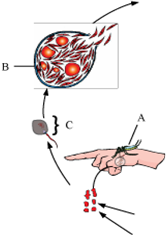
(a) Mention the roles of A in the life cycle of the malarial parasite.
(b) Name the event C and the organ where this event occurs.
(c) Identify the organ B and name the cells being released from it.Write the scientific names of the causal organisms of elephantiasis and ringworm in humans. Mention the body parts affected by them.
