 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow is 'oogenesis' markedly different from 'spermatogenesis' with respect to the growth till puberty in the humans?
Draw a sectional view of human ovary and label the different follicular stages, ovum and Corpus luteum.
Mention any three characteristics of Neanderthal man that lived in near east and central Asia.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Name the technology that has helped scientists to propagate on a large scale the desired crops in a short duration. List the steps carried out to propagate the crops by the said technique.
(b) How are somatic hybrids obtained?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDuring the reproductive cycle of a human female, when, where and how does a placenta develop? What is the function of placenta during pregnancy and embryo development?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDraw a diagram of the microscopic structure of human sperm. Label the following parts in it and write their functions.
(a) Acrosome
(b) Nucleus
(c) Middle piece
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Draw a diagrammatic sectional view of the female reproductive system of human and label the parts:
(i) where the secondary oocytes develop
(ii) which helps in collection of ovum after ovulation
(iii) where fertilization occurs
(iv) where implantation of embryo occurs.
(b) Explain the role of pituitary and the ovarian hormones in menstrual cycle in human females.(a) View of the female reproductive system of human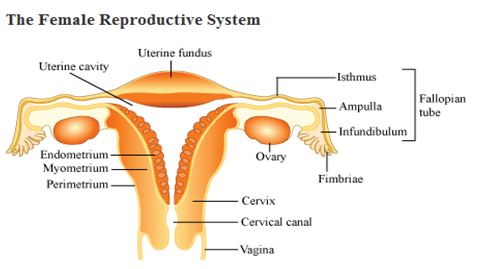
(b) Changes happening in ovary and uterus during menstrual cycle are caused by change in the levels of pituitary and ovarian hormones.
After menstrual phase gonadotropin i.e., Luteinising hormone (LH) and follicular stimulating hormone (FSH) are released from pituitary. Their level gradually increases during follicular phase and it stimulates development of follicles and secretion of estrogen by growing follicles.
Both LH and FSH attain peak on 13th & 14th day.
Rapid secretion LH causes ovulation on day 14.
During luteal phases Graafian follicle changes to corpus luteum which secretes Progesterone Progesterone maintains endometrium which is necessary for implantation.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type