 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite the function of each one of the following:
(a) (Oviducal) Fimbriae
(b) Coleoptile
(c) Oxytocin Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe following is the illustration of the sequence of ovarian events (a to i) in a human female.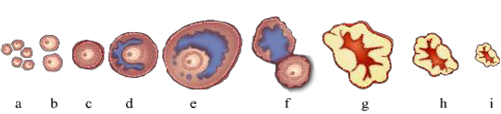
i) Identify the figure that illustrates ovulation and mention the stage of oogenesis it represents.
(ii) Name the ovarian hormone and the pituitary hormone that have caused the above mentioned event.
(iii) Explain the changes that occur in the uterus simultaneously in anticipation.
(iv) Write the difference between c and h.
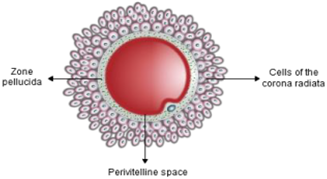
(v) Draw a labeled sketch of the structure of a human ovum prior to fertilization.
(i) Figure 'f' illustrates ovulation. It represents the ovulatory stage of oogenesis.
(ii) The changes that cause ovulation are because of the change in level of the pituitary and ovarian hormones. The pituitary secrets two hormones called Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing hormone (LH). Estrogen is the ovarian hormone released during ovulation. The FSH and LH stimulate follicular development and secretion of estrogen from the primary follicles, the rapid secretion of LH induces graffian follicles to release and release ovum.
(iii) In anticipation of receiving the fertilised egg the primary follicles in the ovary grow to become graffian follicles and simultaneously the endometrium of the uterus regenerates and through proliferation and the blood supply is increased.
(iv) In the figure, (c) stage represents the secondary follicle and the (h) stage represents the degenerating corpus luteum.
|
Secondary follicle |
Corpus luteum |
|
1.It is found in the menstrual stage |
1.It is found in the luteal stage. |
|
2.It is Surrounded by layers of granulosa cells |
2.Layers of granulosa cells are absent |
|
3.Theca layer is present. |
3.No theca layer is present |
How does the megaspore mother cell develop into 7-celled, 8 nucleate embryo sac in an angiosperm? Draw a labeled diagram of a mature embryo sac.
(a) Draw a labelled diagram of the human female reproductive system.
(b) Enumerate the events in the ovary of a human female during:
(i) Follicular phase
(ii) Luteal phase of menstrual cycle
(a) Write the specific location and the functions of the following cells in human males:
(i) Leydig cells
(ii) Sertoli cells
(iii) Primary spermatocyte
(b) Explain the role of any two accessory glands in human male reproductive system.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy are the human testes located outside the abdominal cavity? Name the pouch in which they are present.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Where does fertilization occur in human ? Explain the events that occur during this process.
(b) A couple where both husband and wife are producing functional gametes, but the wife is still unable to conceive, is seeking medical aid. Describe any one method that you can suggest to this couple to become happy parents. Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow is the entry of only one sperm and not many ensured into an ovum during fertilisation in humans?
