 Fill In the Blanks
Fill In the Blanks Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type True Or False
True Or FalseA.
Actin is present in thin filament.B.
H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments.C.
Human skeleton has 206 bones.D.
There are 11 pairs of ribs in man.E.
Sternum is present on the ventral side of the body. Match The Following
Match The Following| A. Smooth muscle | (i) Myoglobin |
| B. Tropomyosin | (ii) Thin filament |
| C. Red muscle | (iii) Sutures |
| D. Skull | (iv) Involuntary |
 One Word Answers
One Word AnswersName the type of joint between the following:
(a) atlas/axis
(b) carpal/metacarpal of thumb
(c) between phalanges
(d) femur/acetabulum
(e) between cranial bones.
(f) between pubic bones in the pelvic girdle.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeMyosin filament : Each myosin (thick) filament is a polymerised monomeric proteins. The monomeric units are called Meromyosins. These constitute make one thick filament.
Each meromyosin has two important parts, a globular head with a short arm and a tail, the former being called the heavy meromyosin (HMM) and the latter, the light meromyosin (LMM). The HMM component, i.e.; the head and short arm projects outwards at regular
distance and angle from each other from the surface of a polymerised myosin filament and is known as cross arm. The globular head is an active ATPase enzyme and has binding sites for ATP and active sites for actin.
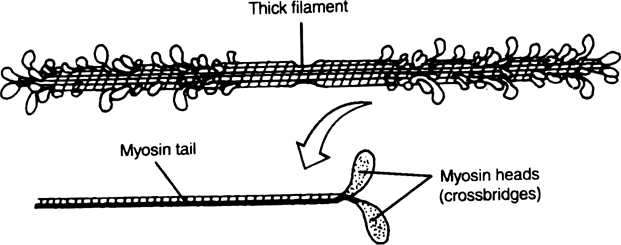
Thick filament (above) and a myosin molecule (below)
