 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe base sequence in one of the strands of DNA is TAGCATGAT.
(i) Give the base sequence of its complementary strand.
(ii) How are these base pairs held together in a DNA molecule?
(iii) Explain the base complementarity rules. Name the scientist who framed this rule.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeTranslation is the process of polymerising amino acid to form a polypeptide chain.
The triplet sequence of base pairs in mRNA defines the order and sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
The process of translation involves the following three steps: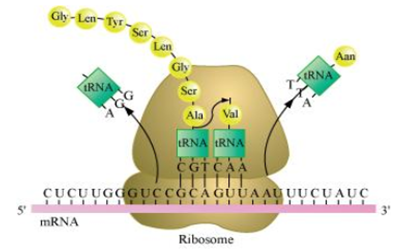
(i) Initiation
(ii) Elongation
(iii) Termination
Describe how the lac operon operates, both in the presence and absence of an inducer in E.coli.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) Draw a neat labelled diagram of a nucleosome.
(b) Mention what enables histones to acquire a positive charge. Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDescribe Frederick Griffith’s experiment on Streptococcus pneumonia. Discuss the conclusion he arrived at.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeFollowing are the features of genetic codes. What does each one indicate ? [2]
Stop codon; Unambiguous codon; Degenerate codon; Universal codon.
