 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeConduction of nerve impulse across a nerve fibre : Conduction of nerve impulse from one nerve fibre to another can be explained in the following points :
1. When the nerve impulse or wave of depolarisation reaches the synaptic knob which has diameter of 50nm, then vesicles of synaptic knobs may release 10,000 acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis under the influence of Ca+2 which diffuse from fluid in synaptic left.
2. The acetylcholine is received by receptors present on the membrane of dendrites of next nerve fibres.
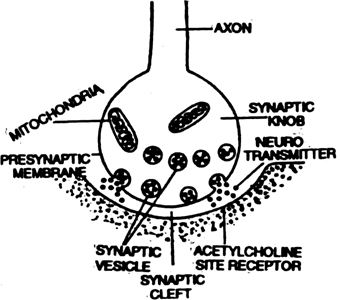
Transmission of Nerve Impulse at Synapse
3. Due to acetylcholine, membrane of dendrites becomes depolarised. Immediately acetylcholine splits into acetic acid and choline by an enzyme acetylcholinesterase are present in the membrane of dendrites.
4. Acetic acid + choline return to synaptic knobs and are converted into acetylcholine for reuse.
In case of sympathetic nerve fibres, the nerve impulse travels from one nerve fibres to next by the release of chemical called adrenaline or nor-adrenalin. Thus, these care adrenergic. The adrenalin or nor-adrenalin is inactivated by monoamine oxidase.
Reverse nerve impulse conduction is not possible because dendrites have no acetylcholine. So, it is one way or unidirectional.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type