 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDistinguish between
(e) cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
|
Cranial Nerves |
Spinal Nerves |
|
1. They arise from brain. 2. They may be sensory, motor or mixed. 3. They are 12 pairs. 4. They may be unbranched or branched. 5. These are not formed by dorsal and ventral roots. 6. They come out formina of skull. |
1. They arise from spinal cord except 1st pair which develops from medulla oblongata. 2. They are mixed. 3. They are 31 pairs. 4. They are branched, each gives 3 branches. 5. They are formed by dorsal and ventral roots. 6. They emere out between intervertebral foramina. |
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsPhotosensitive compound in human eye is made up of
opsin and Retinal
opsin ans Retinol
transducin and Retinene
transducin and Retinene
A diagram showing axon terminal and synapse is given. Identify correctly at least two of A-D.
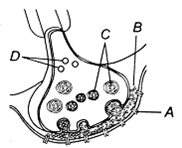
|
A – Receptor |
C – Synaptic vesicles |
|
B – Synaptic connection |
D- K+ |
|
A – Neurotransmitter |
B- Synaptic cleft |
|
A – Neurotransmitter |
B- Synaptic cleft |
Parts A, B, C and D of the human eyes are shown in the diagram. Select the option, which gives correct identification along with its functions/ characteristics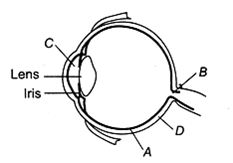
A - retina - contains photoreceptors -rods and cones
B-blind spot- has only a few rods and cones
C - aqueous chamber - reflects the light which does not pass through the lens
C - aqueous chamber - reflects the light which does not pass through the lens
Destruction of the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord would result in loss of
Sensory impulses
Voluntary motor impulses
Commissural impulses
Commissural impulses
In mammalian eye, the 'fovea' is the center of the visual field, where
high density of cones occur, but has no rods.
the optic nerve leaves the eye.
only rods are present
only rods are present
