 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsSelect the statement which explains best parasitism.
One organism is benefited.
Both the organisms are benefited.
One organism is benefited, other is not affected.
One organism is benefited, other is affected.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeStudy the graph given below and answer the questions that follow: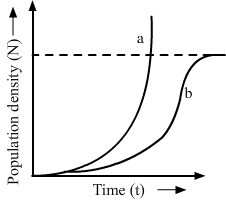
(i) Write the status of food and space in the curves (a) and (b).
(ii) In the absence of predators, which one of the two curves would appropriately depict the prey population?
(iii) Time has been shown on X-axis and there is a parallel dotted line above it. Give the significance of this dotted line.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type'Analysis of age-pyramids for human population can provide important inputs for long-term planning strategies.' Explain.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite the equation that helps in deriving the net primary productivity of an ecosystem.
Explain mutualism with the help of any two examples. How is it different from commensalism?
Mutualism is the interaction which confers benefits on both the interacting species.
For example:
i. Lichens represent an intimate mutualistic relationship between a fungus and photosynthesizing algae or cyanobacteria in which the fungus provides protection to the algae or cyanobacteria and the algae and cyanobacteria provide food to the fungus.
ii. Mycorrhizae are associations between fungi and roots of higher plants. Fungi help the plant in the absorption of essential nutrients from the soil while the plant, in turn provides the fungi with energy-yielding carbohydrates.
In commensalism the interaction where one species is benefitted and the other is neither benefitted nor harmed is called commensalism.
Species Species Name of interaction
A B
+ + Mutualism
+ 0 Commensalism