Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type One Word Answers
One Word Answers Long Answer Type
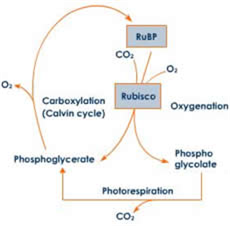
Long Answer TypePhotorespiration is the process where oxygen is consumed, food is oxidized and carbondioxide is liberated, but no energy is produced. It is a highly wasteful process which occurs in the presence of light.
Mechanism of photorespiration:
It takes place in chloroplasts and completes with the assistance of peroxysomes and mitochondria.
1. At high temperature RUBP caThe enzyme has great affinity for oxygen than for carbon dioxide. It combines oxygen and RUBP to form PGA and phosphoglycolate.
2. Phosphoglycolate forms phosphoric acid and glycolate in the presence of hydrolase. It passes into peroxysome.
3. Glycolate molecule combines with oxygen to form glyoxylate and H2O2 which is very toxic. It occurs in peroxysome.
4. Glycoxylate undergoes amination to form glycine. The glycine molecules undergo condensation, decarboxylation, deamination to form serine.
5. Serine undergoes deamination to form PGA which enters into chloroplast and takes part in C3 cycle. Thus, it is linked with C3 cycle. Moreover RUBP carboxylase changes its behaviour at high temperature and acts RUBPoxygenase and thus it delinks from C3 cycle.