 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) GA3 is applied to rice seedlings.
(b) Dividing cells stop differentiating.
(c) A rotten fruit gets mixed with urripe fruits.
(d) You forget to add cytokinin to the culture medium
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeOpen growth : It is a type of growth where in new cells are always being added to the plant body by the activity of the meristem.
Growth is considered to be open. Plant growth is unique because plants retain the capacity for unlimited growth throughout their life. The meristems present in different locations have the capacity to divide and self-perpetuate. The daughter cells may lose the capacity to divide and such cells make up the plant body. ns in which they are formed.
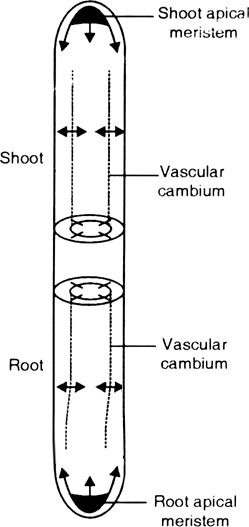
Diagrammatic representation of locations of root apical meristem, shoot apical meristem and vascular cambium. Arrows exhibit the direction of growth of cells and organ
Differentiation in plants is open, because cells/tissues arising out of the same meristem have different structures at maturity. The location also decides the final
structure of a cell/tissue at maturity. For example, cells positioned away from root apical
meristems differentiate as root-cap cells, while those pushed to the periphery mature as epidermis.
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsMatch the following and select the correct answer.
|
Column I |
Column II |
||
|
A. |
Centriole |
1. |
Infolding in mitochondria |
|
B. |
Chlorophyll |
2. |
Thylakoids |
|
C. |
Cristae |
3. |
Nucleic acid |
|
D. |
Ribozymes |
4. |
Basal body cilia of flagella |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
4 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
1 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
4 |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
4 |
A few normal seedlings of tomato were kept in a dark room. After a few days they were found to have become white - coloured like albinos. Which of the following terms will you use to describe them?
Mutated
Embolised
Etiolated
Etiolated
Which one of the following growth regulators is known as stress hormone?
abscsic acid
Ethylene
GA3
GA3
