 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain the law of independent assortment with a dihybrid cross.
Result of dihybrid cross.
Dihybrid cross. A cross in which two characters are taken into consideration during experimentation, such a cross is called dihybrid cross. A cross between a pea plant with yellow smooth and a pea plant with green, wrinkled seeds are considered.
Explanation. When a cross is made between pea plant having yellow smooth seeds (YYSS) and a pea plant with green wrinkled seeds (yyss). At the time of cross pollination, yellow smooth (YYSS) produce gametes with genes (YS) and green wrinkled will produce gametes with gene (ys). Gametes unite at random. The seeds obtained when placed in soil will grow to form plants and produce seeds which are yellow smooth (YySs) because yellow and smooth characters are dominant over green and wrinkled. These are called as plants of F1 generation.
When plants of F1 generation are allowed to self pollinate gametes formed YS, Ys, yS and ys by meiosis, they unite at random forming seeds. The plants thus obtained were called as F2 generation. They are Yellow smooth (YYSS, YySS, YsSS, YYSs); yellow wrinkled (YYss, Yyss), green smooth (yySS, yySs) and green wrinkled (yyss) in the ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 :1. The result of dihybrid cross can be shown in Fig. 1.12 in the chequer board.
From the above dihybrid cross, it can be derived that each gene is assorted independently of the other during its passage from one generation to the other or Law of independent assortment is justified.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIn four o’clock plants, red colour (R) is incompletely dominant over white (r), thus the heterozygous has pink colour. What will be the offspring in a cross between red flower and a pink flower plant?
A man with blood group A married a woman with B group. They have a son with AB blood group and a daughter with blood group O. Work out the cross and show the possibility of such inheritance.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeA homozygous tall pea plant with green seeds is crossed with a dwarf pea plant with yellow seeds.
(i) What would be the phenotype and genotype of F1.
(ii) Work out the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation with the help of a Punnet square.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHaemophilia is a sex linked recessive disorder of humans. The pedigree chart given below show the inheritance of haemophilia in one family. Study the pattern of inheritance and answer the questions given.
(a) Give all the possible genotypes of the members 4, 5 and 6 in the pedigree chart.
(b) A blood test shows that the individual 14 is a carrier of haemophilia. The member numbered 15 has recently married the member numbered 14.
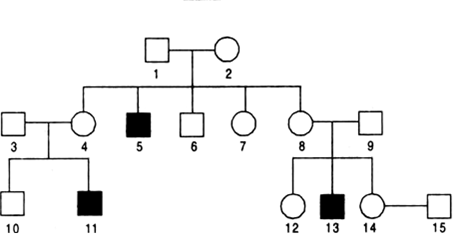
What is the probability that their first child will be a haemophilic male?
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions