 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeMention any two contrasting traits with respect to seeds in pea plant that were studied by Mendel.
In Snapdragon, A cross between true breeding red flower (RR) plants and true breeding white flower (rr) plants showed a Progeny of plants with all pink flowers.
(a)The appearance of pink flowers is not known as blending. Why?(b)What is the phenomenon known as?
Linkage or crossing-over of genes are alternatives of each other. Justify with the help of an example.
Why is pedigree analysis done in the study of human genetics? State the conclusions that can be drawn from it.
Identify ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’, ‘e’ and ‘f’ in the table given below :
|
No. |
Syndrome |
Cause |
Characteristic of affected individuals |
Sex Male/Female/ both |
|
1 |
Down’s |
Trisomy of 21 chromosome |
‘a’ (i) (ii) |
‘b’ |
|
2 |
‘c’ |
XXY |
Overall masculine development |
‘d’ |
|
3 |
Turner |
45 with XO |
‘e’ (i) (ii) |
‘f’ |
Name the respective pattern of inheritance where F1 phenotype
(a) does not resemble either of the two parents and is in between the two.
(b) resembles only one of the two parents.
(a) Explain the phenomena of multiple allelism and co-dominanace taking ABO blood group as an example.
(b) What is the phenotype of the following:(i) IAi
(ii) i i
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Explain a monohybrid cross taking seed coat colour as a trait in Pisum sativum. Work out the cross upto F2 generation.
(b) State the laws of inheritance that can be derived from such a cross.
(c) How is the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation different in a dihybrid cross?
(a) Monohybrid cross is the cross in which only one trait is taken into account.
For example, if pea plant with yellow seed coat is crossed with pea plant having green seed coat then in the F1 generation all the plants produce yellow seeds.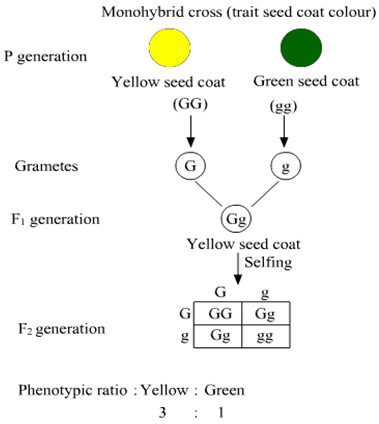
(b) Two laws can be derived from such a cross
Law of Dominance- According to this law, characters are controlled by discrete units called factors, which occur in pairs with one member of the pair dominating over the other in a dissimilar pair. It explains the expression of only one of the parental character in F1generation and expression or appearance of both in F2 generation.
In the given cross, the allele for yellow seeds is dominant over the allele that produces green seeds. In F1 generation all offsprings showed yellow colour of seed (dominant character) and expression of both yellow and green in F2 generation.
Law of Segregation-This law states that the two alleles of a pair segregate or separate during gamete formation such that a gamete receives only one of the two factors. In homozygous parents, all gametes produced are similar; while in heterozygous parents, two kinds of gametes are produced in equal proportions. The alleles for yellow and green seeds in the F1 generation segregate and the gamete either contains yellow allele or green allele giving rise to different combination in the F2 generation. Thus, showing that the gametes receive only one of the two factors.
(a) Why is fertilization in an angiosperm referred to as double fertilisation? Mention the ploidy of the cells involved.
(b) Draw a neat labeled sketch of L.S. of an endospermous monocot seed.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA male honeybee has 16 chromosomes whereas its female has 32 chromosomes. Give one reason.
