 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) What is polygenic inheritance ? Explain with the help of a suitable example.
(b) How are pleiotropy and Mendelian pattern of inheritance different from polygenic pattern of inheritance ?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeGive an example of an autosomal recessive trait in humans. Explain its pattern of inheritance with the help of a cross.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeA. Why is haemophilia generally observed in human males? Explain the conditions under which a human female can be haemophilic.
B. A pregnant human female was advised to undergo M.T.P. It was diagnosed by her doctor that the foetus she is carrying has developed from a zygote formed by an XX egg fertilized by Y-carrying sperm. Why was she advised to undergo M.T.P.?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDuring a medical investigation, an infant was found to possess an extra chromosome 21. Decribe the symptoms the child is likely to develop later in the life.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeState and explain the ‘law of independent assortment’ in a typical Mendelian dihybrid cross.
Law of Independent Assortment (Third law) is based on inheritance of two genes, i.e. dihybrid cross which states that when two pairs of contrasting traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters. These factors randomly rearrange in the offspring producing both parental and new combination of characters means inheritance of one character does not affect the inheritance of another character and both characters
assort independently. The Punnett square can be used to understand the independent segregation of the two pairs of genes during meiosis. Linkage is the exception of law of independent assortment.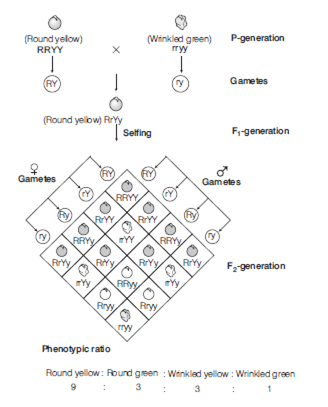
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeGive a scientific term:
Exhibition of superiorityof the hybrid over both of its parents
