 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn which one of the following sets of three items each belong to the category mentioned against them
Lysine, glycine, thiamine - amino acids
Myosin, oxytocin and gastrin - hormones
Rennin, helicase and hyaluronidase - enzymes
Optic nerve, oculomotor, vagus - sensory nerves
Given below is a highly simplified representation of the human sex chromosomes from a karyotype
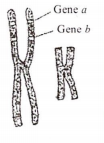
The gene a and b could be of
colour blindness and body height
attached ear lobe and Rhesus blood group
haemophilia and red-green colour blindness
phenylketonuria and haemophilia
Genes present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells are found in
mitochondria and inherited via egg cytoplasm
lysosomes and peroxisomes
Golgi bodies and smooth endoplasmic reticulum
plastids and inherited via male gamete
Given below is a pedigree chart showing the inheritance ofa certain sex-linked trait in humans
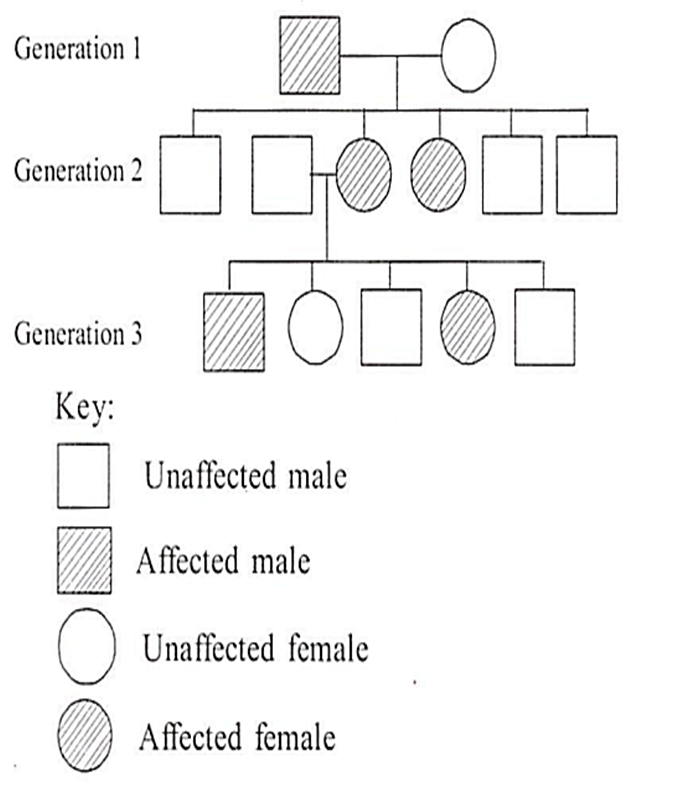
The trait traced in the above pedigree chart is
dominant X- linked
recessive X- linked
dominant Y- linked
recessive Y- linked
The "cri-du-chat" syndrome is caused by change in chromosome structure involving
deletion
duplication
inversion
translocation
Grain colour in wheat is determined by three pairs of polygenes. Following the cross AABBCC (dark colour) x aabbcc (light colour), in F2 generation what proportion of the progeny is likely to resemble either parent?
None
Less than 5 percent
One third
Half
B.
Less than 5 percent
Polygene results in quantitative inheritance. Quantitative inheritance is characterised by occurrence of intermediate forms between the parental type. There will be 7 (1 : 6 : 15 : 20 : 15 : 6 : 1) phenotypes when three polygene pairs are involved. The total number of progeny would be 64. Out of these sixty four only two will be likely to resemble either parents. Hence their proportion in F2 generation would be 3.12 i.e. less than 5%.
Primary source of allelic variation is
independent assortment
recombination
mutation
polyploidy
Assertion: Polytene chromosomes have a high amount of DNA.
Reason: Polytene chromosomes are formed by repeated replication of chromosomal DNA without separation of chromatids.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
A baby has been born with a small tail. It is a case exhibiting
retrogressive evolution
mutation
atavism
metamorphosis
Given below is a pedigree chart of a family with five children. It shows the inheritance of attached ear-lobes as opposed to the free ones. The squares represent the male individuals and circles the female individuals. Which one of the following conclusions drawn is correct
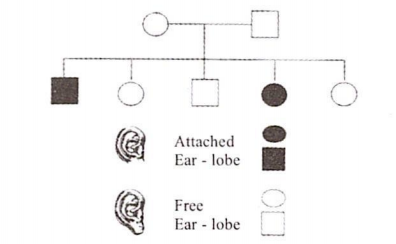
The parents are homozygous recessive.
The trait is Y-linked.
The parents are homozygous dominant.
The parents are heterozygous.
