 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions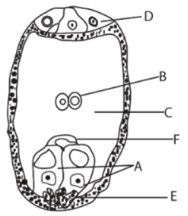
In the given diagram, parts labelled as A, B, C, D, E and F are respectively identified as
Synergids, polar nuclei, central cell, antipodals, filiform apparatus and egg
Polar nuclei, egg, antipodals, central cell, filiform apparatus and synergids
Egg, synergids, central cell, filiform apparatus, antipodals and polar nuclei
Central cell, polar nuclei filiform apparatus, antipodals, synergids and egg
When two unrelated individuals or lines are crossed, the performance of F1 hybrid in often superior to both of its parents. This phenomenon is called
Transformation
Heterosis
Splicing
Meta Morphosis
An irregular mode of reproduction resulting in the development of an embryo without fertilization is called
(I) parthenogenesis
(II) apogamy
(III) sporophytic budding
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Only I
Only II
II and III
I, II and III
Compare the statement I and II and choose the correct option.
Statement I In the flowering plants due to higher accumulation of auxins dormancy of lateral buds occurs.
Statement II In Maryland Mammoth (a tobacco variety) flowering occurred at a different time at different latitude due to gibberellins concentration.
Statement I is true, but II is false
Statement I is false, but II is true
Both statements are true
Both statements are false
Which one of the given pollination technique/adaptation is different than others?
Herkogamy
Geitonogamy
Dichogamy
Heterostyly
B.
Geitonogamy
Geitonogamy is a technique of self-pollination, in which pollen of one flower is deposited on the stigma of another flower of the same plant. While others are mechanisms adopted by bisexual flowers to avoid self-pollination and promote Cross-pollination.
• Dichogamy The condition where the maturing time of anther and stigma is different. Anther matures first, i.e.protandry, stigma matures first, i.e. protogyny.
• Herkogamy Includes mechanical barrier in flower to ensure cross-pollination.
• Heterostyle The height of stigma and Anther is different to avoid self-pollination.
The one advantage of cleistogamy is
It leads to greater genetic diversity
Seed dispersal is more efficient and wide spread
seed set is not dependent on pollinators
Each visit of pollinator results in the transfer of hundreds of pollen grains
In gymnosperms, the pollen chamber represents
A cell in the pollen grain in which the sperms are formed
A cavity in the ovule in which pollen grains are stored after pollination
An opening in the megagametophyte through which the pollen tube approaches the egg
The microsporangium in which pollen grains develop
