Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow are the following conversions carried out?
Methyl magnesium bromide → 2-Methylpropan-2-ol.
Give the structure and IUPAC name of the expected product of the following reaction:
Catalytical reduction of butanal.
Give the structure and IUPAC name of the expected product of the following reaction:
Hydroboration of but-1-ene.
Give the structure and IUPAC name of the expected product of the following reaction:
Hydration of propylene in presence of dil. sulphuric acid.
Give the structure and IUPAC name of the expected product of the following reaction:
Reaction of propanone with methylmagnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis.
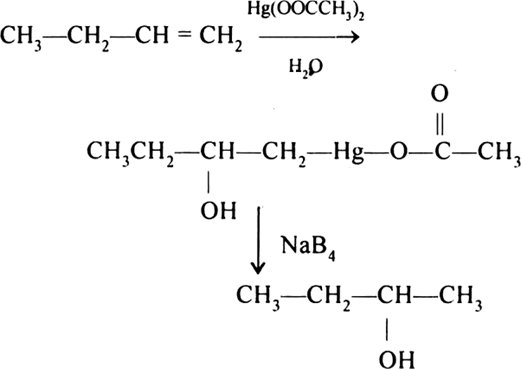
Explain Oxymercuration and demercuration.
The following is not an appropriate reaction for the preparation of t-butyl ethyl ether.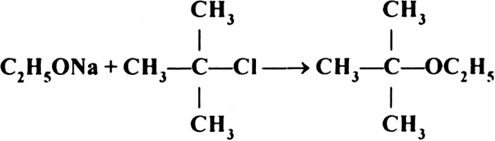
(i) What would be the major product of this reaction?
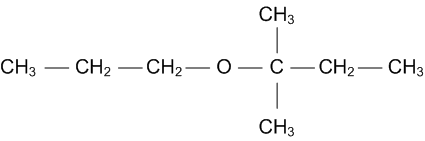
(ii) Write a suitable reaction for the preparation of t-butyl ethyl ether.
Give the major products that are formed by heating each of the following ethers with HI.![]()
Give the major products that are formed by heating each of the following ethers with HI.