 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypePhenol is very weak acid. Phenol can lose a hydrogen ion and forms phenoxide ion. The negative charge on the oxygen atom is delocalised around the ring and thus stblilised. Hence lesser the acidity.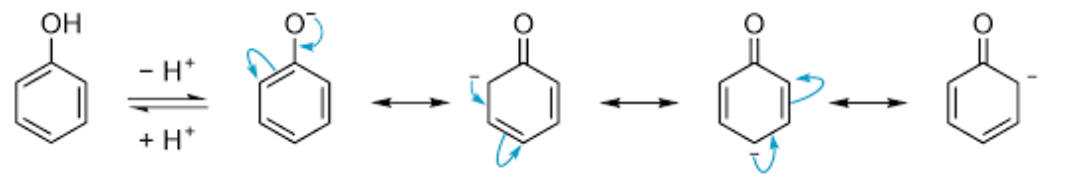
The resonance structures of phenoxide ions explain the delocalization of negative charge. In case of substituted phenols, acidity of phenols increases in the presence of electron withdrawing group. This is due to the stability of the phenoxide ion generated. The acidity of phenols further increases if these groups are attached at ortho and para positions. This is due to the fact that the negative charge in phenoxide ion is mainly delocalized at ortho and para positions of the attached benzene ring. On the other hand, the acidity of phenols decreases in presence of electron donating groups as they prohibit the formation of phenoxide ion.
Write chemical equations for what happens when:
(i) 2-methyl-2-proponal vapours are passed over heated copper.
(ii) A Triglyceride is treated with sodium hydroxide solution.
Which alcohol is known as wood alcohol? How will you prepare it commercially? Give its one use?
