 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsReaction of formaldehyde and ammonia gives
hexamethylene tetramine
bakelite
urea
triethylene tetramine
Which of the following compounds is not formed in iodoform reaction of acetone?
CH3COCH2I
ICH2COCH2I
CH3COCHI2
CH3COCI3
A compound (A) C4H8Cl2 on alkaline hydrolysis to give compound (B) C4H8O which gives an oxime and positive Tollen's reagent test. What is the structure of (A)?
CH3CH2CH2CHCl2
CH3CCl2CH2CH3
CH3CH(Cl)CH(Cl)CH3
CH2ClCH2CH2CH2Cl
In the reaction,
CH3-CH2-Cl (A) (B), end product (B) is
CH3 - CH2 - CN
CH3 - CH2 - CONH2
CH3 - CH2 - COOH
CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CN
A colourless water soluble organic liquid decomposes sodium carbonate and liberates CO2. It produces black ppt with Tollen's reagent. The liquid is
acetaldehyde
acetamide
formic acid
acetone
Order of ease of decarboxylation of the following acids is
(i) CH3COOH
(ii) CH2=CH-CH2.COOH
(iii) CH2(COOH)2
(iv) 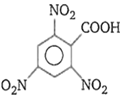
i > ii > iii > iv
iii > iv > ii > i
iv > iii > ii > i
i > iii > ii > iv
In keto-enol tautomerism of dicarbonyl compounds, the enol-form is preferred in contrast to the keto-form, this is due to
presence of carbonyl group on each side of -CH2 group
resonance stabilisation of enol form
presence of methylene group
rapid chemical exchange
