Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy is benzaldehyde is less reactive than acetaldehyde towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
Account for the following:
(i) Formaldehyde gives Cannizzaro’s reaction whereas acetaldehyde does not.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl compounds.
Account for the following:
(i) Chloroacetic acid has higher pKa value than acetic acid.
(ii) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta position.
(iii) Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeHow would you obtain the following named sources:
(i) Tertiary butyl alcohol from acetone? (ii) Acetone from acetic acid?
Mention conditions for reactions involved.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain why O-hydroxy benzaldehyde is a liquid at room temperature while p- hydroxy benzaldehyde is a high melting solid.
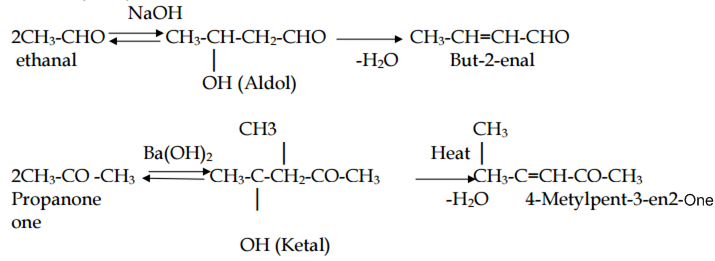
Describe the following with an example:
Aldol condensation
Aldehydes and ketones having at least one α-hydrogen condense in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form β-hydroxy alddil ehydes (aldol) or β-hydroxy ketones (ketol).