 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow do you prepare:
(i) K2MnO4 from MnO2?
(ii) Na2Cr2O7 from Na2CrO4?
i) K2MnO4 can be prepared from pyrolusite (MnO2). The ore is fused with KOH in the presence of either atmospheric oxygen or an oxidising agent, such as KNO3 or KClO4, to give K2MnO4.
2 MnO2 + 4 KOH + O2 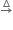 2 K2MnO4 +2H2O
2 K2MnO4 +2H2O
green
ii) Na2Cr2O7 can be prepared from Na2CrO4 in the following way:
For the preparation of sodium dichromate, the yellow solution of sodium chromate is acidified with sulphuric acid to give a solution from which orange sodium dichromate, Na2Cr2O7.2H2O can be crystallised.
Balanced equation for above reactions is as follows:
2 Na2CrO4 + 2H+ ---> Na2Cr2O7 + 2 Na+ + H2O
Account for the following:
(i) Mn2+ is more stable than Fe2+ towards oxidation to +3 state.
(ii) The enthalpy of atomization is lowest for Zn in 3d series of the transition elements.
(iii) Actinoid elements show a wide range of oxidation states.
(i) Name the elements of 3d transition series that show a maximum number of oxidation states. Why does this happen?
(ii) Which transition metal of 3d series has positive E0 (M2+/M) value and why?
(iii) Out of Cr3+ and Mn3+, which is a stronger oxidising agent and why?
(iv) Name a member of the lanthanoid series that is well-known to exhibit +2 oxidation state.
(v) Complete the following equation: MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- -->
Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength in aqueous solution:
CH3NH2, (CH3)3N, (CH3)2NH
What happens when
(i) PCl5 is heated?
(ii) H3PO3 is heated?
Write the reactions involved ?
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Bond enthalpy of F2 is lower than that of Cl2.
(ii) PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3Account for the following:
(i) Helium is used in diving apparatus.
(ii) Fluorine does not exhibit positive oxidation state.
(iii) Oxygen shows catenation behaviour less than sulphur
