 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypePb(NO3)2 on heating gives a brown gas which undergoes dimerization on cooling ? Identify the gas.
Write the structures of the following:
i) BrF3
ii) XeF4
Or
What happens when:
i) SO2 gas is passed through an aqueous solution Fe3+ salt ?
ii) XeF4 reacts with SbF5 ?
Give reasons:
i) SO2 is reducing while TeO2 is an oxidizing agent.
ii) Nitrogen does not form pentahalide.
iii) ICl is more reactive than I2
i) Name the method of refining of nickel
ii) what is the role of cryolite in the extraction of aluminium
iii) what is the role of limestone in the extraction of iron from its oxides ?
The elements of 3d transition series are given as:
Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn
Answer the following:
i) Write the element which shows a maximum number of oxidation states.Give reason.
ii) Which element has the highest m.p?
iii) Which elements shows only +3 oxidation state ?
iv) which element is a strong oxidising agent in +3 oxidation state and why?
How would you account for the following?
(i) NF3 is an exothermic compound but NCl3 is not.
(ii) The acidic strength of compounds increases in the order:
PH3 < H2S < HCl
(iii) SF6 is kinetically inert. Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) (HPO3)3
(ii) BrF3
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) HgCl2 + PH3-->
(ii) SO3 + H2SO4 -->
(iii) XeF4 + H2O -->
OR
(a) What happens when?
(i) Chlorine gas is passed through a hot concentrated solution of NaOH?
(ii) Sulphur dioxide gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a Fe (III) salt?
(b) Answer the following:
(i) What is the basicity of H3PO3 and why?
(ii) Why does fluorine not play the role of a central atom in inter-halogen compounds?
(iii) Why do noble gases have very low boiling points?
(i) (HPO3)3
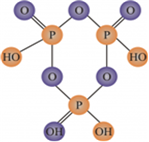
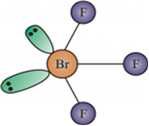
(ii) BrF3 has a bent T-shape and can be drawn as follows.
(b)
(i) 3 HgCl2 + 2 PH3 --> Hg3P2 + 6 HCl
(ii) SO3 + H2SO4 ---> H2S2O7
(iii) 6 XeF4 +12 H2O ---> 4Xe + 2 XeO3 + 24 HF + 3O2
Or
(a)
(i) When chlorine is passed through a hot concentrated solution of NaOH, it undergoes disproportionation in which chlorine is simultaneously reduced to Cl-and is oxidised to
3Cl2 + 3NaOH --> 5NaCl + NaClO3 + 3H2O
(ii) SO2 acts as a reducing agent when passed through an aqueous solution containing Fe(III) salt. It reduces Fe(III) to Fe(II) i.e., ferric ions to ferrous ions.
2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O ---> 2Fe2+ + SO42-+ 4H+
(b)
(i) Basicity of H3PO3 depends upon the number of ionizable -OH groups present in the molecule. That is the number of hydrogen attached to the electronegative atom oxygen.
H3PO3 has two ionizable –OH group, thus its basicity is 2
The structure of H3PO3 follows as: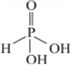
(ii) Fluorine does not play the role of a central atom in inter-halogen compounds because of the absence of d- orbital. Also, because of the small size of fluorine, it cannot accommodate larger halogen groups.
(iii) The noble gases have low boiling point due to the fact that the noble gases are mono atomic. Having no interatomic forces except weak dispersion forces.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type