 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeUsing integration, find the area of the triangular region whose sides have the equations y = 2 x + 1, y = 3 x + 1 and x = 4.
The equations of the sides are
2 x + y - 4 = 0 ...(1)
3 x - 2 y - 6 = 0 ...(2)
x - 3 y + 5 = 0 ...(3)
Solving (1) and (2), we get
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solving (2) and (3), we get,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solving (1) and (3), we get,
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]()
From B. draw BL ⊥ x-axis and from A. draw AM ⊥ x-axis.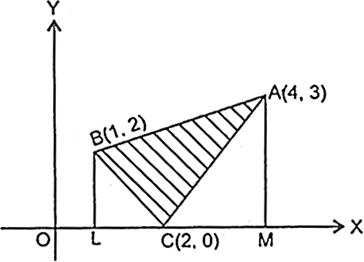
Required area = Area of ![]() = Area of region BLMA - area of
= Area of region BLMA - area of ![]() - area of
- area of ![]()
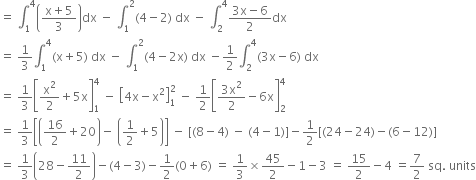
Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (-1, 1), (0, 5) and (3, 2).
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeUsing integration, find the area of the region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (1, 0), (2, 2) and (3, 1).
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeUsing integration find the area of region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (-1, 0), (1, 3) and (3, 2).
