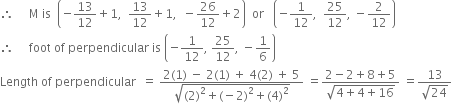Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe equation of plane is
2x – 2y + 4 z + 5 = 0 ...(1)
Direction ratios of the normal to the plane are
2,–2, 4 i.e., 1,– 1, 2.
Let M be foot of perpendicular from P (1, 1, 2) to the plane.
Now PM is a straight line which passes through P (1. 1,2) and has direction ratios as 1, – 1, 2.
∴ its equations are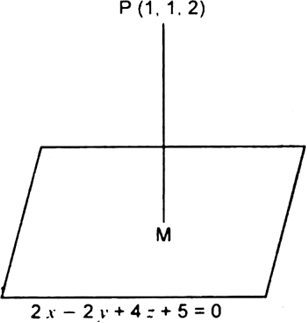
![]()
Any point M on line is (r + 1, – r + 1, 2 r + 2)
∵ M lies on plane (1)
∴ 2 (r + 1) – 2 (– r + 1) + 4 (2 r + 2) + 5 = 0.
∴ 2r + 2 + 2r – 2 + 8r + 8 + 5 = 0![]()