 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich one of the following is a matching pair?
Lubb - sharp closure of AV valves at the beginning of ventricular systole
Dup - sudden opening of semilunar valves at the beginning of ventricular diastole
Pulsation of the radial artery - valves in the blood vessels
Initiation of the heart beat - Purkinje fibres
Assertion : Smaller the organism higher is the rate of metabolism per gram weight.
Reason : The heart rate of a six month old baby is much higher than that of an old person.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false statements
Which proteolytic enzyme induces lysis of fibrin during fibrinolysis ?
Fibrin
Thrombin
Plasmin
Platelet factor-VII
The first heart sound is produced when :
diastole begins
semilunar valve close quickly
interventricular pressure decreases
bicuspid and tricuspid valve close quickly
Which of the following layer of heart wall consists of cardiac muscles ?
Endocardium
Myocardium
Epicardium
All of these
If heart beats 75 beats/min. then what is time for cardiac cycle ?
0.5 sec
0.8 sec
1 sec
1.5 sec
Blood pressure increases and heart rate decreases in response to :
exercise
haemorrhage
exposure to high altitude
increased intracranial pressure
'P' wave of ECG occurs before the:
onset of ventricular ejection
end of atrial contraction
begining of atrial contraction
none of the above
C.
begining of atrial contraction
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed over the skin.
Each peak in the ECG is identified with a letter from P to T that corresponds to a specific electrical activity of the heart.
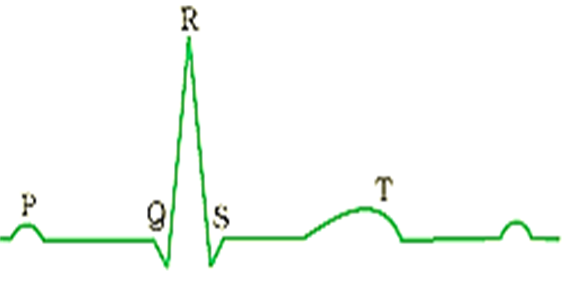
P- wave represents the electrical excitation or depolarisation of the atria. It is the first upward deflection caused by the passage of the action current over the auricles. Its average duration is about 0.1 sec.
QRS complex represents depolarisation of ventricles.
T- wave represents return of the ventricles from excited to normal state.
In which form CO2 is mostly carried by blood
bicarbonate
carbonic acid
Carbamino compound
Carboxyhaemoglobin
