 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe figure shows a diagrammatic view of the human respiratory system with label A, B, C and D. Select the option. Which gives correct identification and main function and /or characteristic.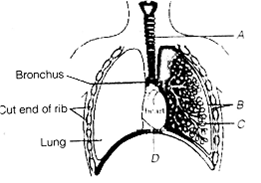
A - trachea - long tube supported by complete cartilaginous rings for conducting inspired air.
B - pleural membrane - surround ribs on both sides to provide cushion against rubbing
C - alveoli - thin walled vascular bag - like structure for exchange of gases
C - alveoli - thin walled vascular bag - like structure for exchange of gases
Figure shows schematic plan of blood circulation in human with labels A to D. Identify to label and give its function/s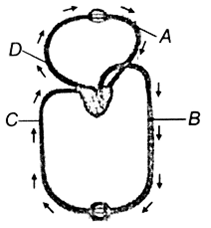
A - pulmonary vein - takes impure blood from body parts,pO2 = 60 mmHg
B - pulmonary artery - takes blood from heart to lungs, pO2 = 90 mmHg
C - vena cava - takes blood from body parts to right auricle, pCO2 = 45 mmHg
C - vena cava - takes blood from body parts to right auricle, pCO2 = 45 mmHg
Name the pulmonary disease in which alveolar surface area involved in gas exchange is drastically reduced due to damage in the alveolar walls.
Pleurisy
Emphysema
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Both A and B antigens on RBC but no antibodies in the plasma
Both A and B antibodies in the plasma
No antigen or RBC and no antibody in the plasma
No antigen or RBC and no antibody in the plasma
Which one of the following is the correct statement for respiration in humans?
Cigarette smoking may lead to inflammation of bronchi
Neural signals from pneumotoxic centre in pons region of brain can increase the duration of inspiration
Workers in grinding and stone-breaking industries may suffer, from lung fibrosis.
Workers in grinding and stone-breaking industries may suffer, from lung fibrosis.
In which one of the following processes CO2 is not released?
Aerobic respiration in plants
Aerobic respiration in animals
Alcoholic fermentation
Alcoholic fermentation
When you hold your breath, which of the following gas changes in blood would first lead to the urge to breathe?
Falling O2 concentration
Rising CO2 concentration
Falling CO2 concentration
Falling CO2 concentration
Two friends are eating together on a dining table. One of them suddenly starts coughing while swallowing some food. This coughing would have been due to improper movement of
Diaphragm
Neck
Tongue
Tongue
The figure given below shows a small part of human lung where exchange of gases takes place. In which one of the options given below, the one part A, B, C or D is correctly identified along with its function.
A: Alveolar cavity - main site of exchange of respiratory gases
D: Capillary wall - exchange of O2 and CO2 takes place here
B : Red blood cell - transport of CO2 mainly
B : Red blood cell - transport of CO2 mainly
A large proportion of oxygen is left unused in the human blood even after its uptake by the body tissue. This O2
Raise the pCO2 of blood 75 mm of Hg.
Is enough to keep oxyhaemoglobin
helps in releasing more O2 to the epithelial tissues
helps in releasing more O2 to the epithelial tissues
