 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe IUPAC name of the compound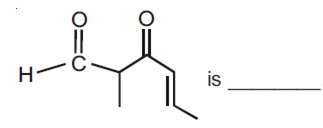
3-keto-2-methylhex-4-enal
5-formylhex-2-en-3-one
5-methyl-4-oxohex-2-en-5-al
5-methyl-4-oxohex-2-en-5-al
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their
Formation of intramolecular H-bonding
Formation of intermolecular H-bonding
Formation of intermolecular H-bonding
More extensive association of carboxylic acid via Vander Waals force of attraction
Compound A, C8H10O, is found to react with NaOI (produced by reacting Y with NaOH) and yields a yellow precipitate with characteristic smell. A and Y are respectively
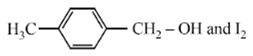
![]()
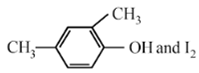
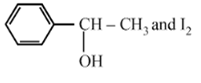
The product of acid hydrolysis of (P) and (Q) can be distinguished by

Lucas reagent
2,4-DNP
Fehling's solution
NaHSO3
C.
Fehling's solution
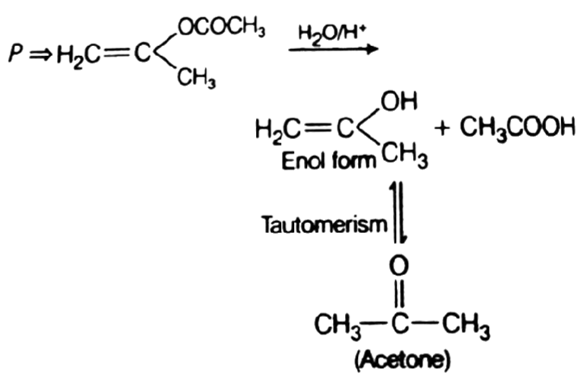
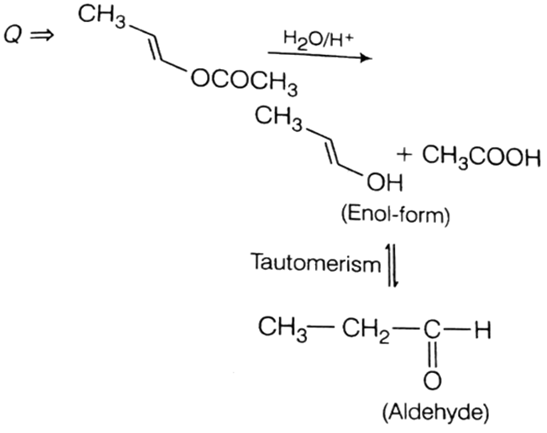
Because Fehling solution cannot be reduced with acetone. Thus, used to differentiate ketone (acetone) and aldehyde.
Clemmensen reaction of the ketone is carried out in the presence of
LiAlH4
Zn-Hg with HCl
glycol with KOH
H2 with Pt as a catalyst
Consider the following compounds
Cl3C - COOH Br3C - COOH I3C - COOH
(I) (II) (III)
The decreasing order of decarboxylation is
I > II > III
III > II > I
III > I > II
II > I > III
Sugars are seperated by using the solvent BAW (n-butanol acetic acid -HO) and detected by spraying the plate with
aniline hydrogen phthalate solution
hydrogen peroxide solution
crystals of I2
cupric oxide
