 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsOne end of a massless spring of constant 100 N /m and natural length 0.5 m is fixed and the other end is connected to a particle of mass 0.5 kg lying on a frictionless horizontal table. The spring remains horizontal. If the mass is made to rotate at angular velocity of 2 rad/s, then elongation of spring is
0.1 m
10 cm
1 cm
0.01 cm
A block of mass 2 kg is pushed against a rough vertical wall with a force of 40 N, coefficient of static friction being 0.5. Another horizontal force of 15 N, is applied
on the block in a direction parallel to the wall. If the block will move, then its direction would be
15o with 15 N force
53o with 15 N force
45o with 15 N force
75o with 15N force
B.
53o with 15 N force
Now, When a force of 40N is applied, it will be balanced by the normal reaction from the wall
The net force =
= 625
F = 25 N
This is greater than the 20N (friction), therefore block will move
∴ Direction
=
∴
So, the block will move at an angle 53° with the 15 N force.
Two wires are stretched through same distance. The force constant ofsecond wire is half as that of the first wire. The ratio of work done to stretch first wire and second wire will be
2 : 1
1 : 2
3 : 1
1 : 3
A light string passes over a frictionless pulley. To one of its ends a mass of 8 kg is attached. To its other end two masses of 7 kg each are attached. The acceleration of the system will be
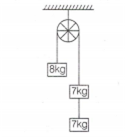
10.2 g
5.10 g
20.36 g
0.27 g
A sphere of mass m moving with velocity v hits inelastically with another stationary sphere of same mass. The ratio of their final velocities will be (in terms of e)
A ball impinges directly on a similar ball at rest. The first ball is brought to rest by the impact. If half of the kinetic energy is lost by impact, the value of coefficient of restitution is
1 / 2√2
1 / √3
1 / √2
√3 / 2
A transformer with efficiency 80% works at 4 kW and 100 V. If the secondary voltage is 200 V, then the primary and secondary currents are respectively
40 A and 16 A
16 A and 40 A
20 A and 40 A
40 A and 20 A
Same spring is attached with 2 kg, 3 kg and 1 kg blocks in three different cases as shown in figure. If x1 , x2, x3 be the extensions in the spring in the three cases, then
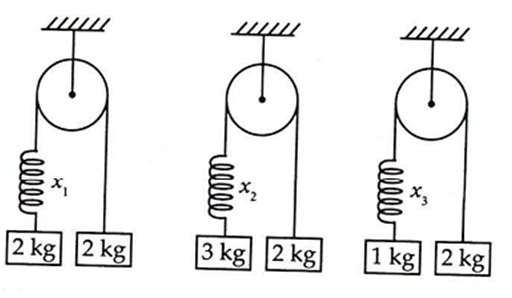
x1 = 0, x3 > x2
x1 > x2 > x3
x3 > x2 > x1
x2 > x1 > x3
Assertion: A particle strikes head-on with another stationary particle such that the first particle comes to rest after collision. The collision should necessarily be elastic.
Reason: In elastic collision, there is a loss of momentum ofthe system of the particles.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Work done in moving a body over a closed loop is zero for every force in nature.
Reason: Work done does not depend on nature of force.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
