 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsPhenol gives characteristic colouration with
iodine solution
bromine water
aqueous FeCl3 solution
ammonium hydroxide
In the following sequence of reactions
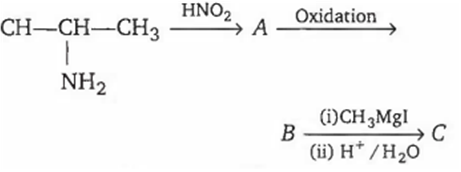
The compound C formed will be
butanol-1
butanol-2
2-methyl propanol-1
1, 1-dimethylethanol
The correct order of dehydration of alcohols is
1° > 2° > 3°
3° > 2° > 1°
2° > 1° > 3°
1° > 3° > 2°
Ethanolic KOH gives
dehalogenation reactions
dehydrogenation reactions
dehydrohalogenation reactions
substitution reactions
Which alcohol will give immediate turbidity on shaking with HCl at room temperature?
3-methyl pentan-2-ol
2-methyl butan-1-ol
Butan-3-ol
2-methylpropan-2-ol
Which of the following ether is formed from alcohol and diazomethane?
1-ethoxypropane
ethoxyethane
1-methoxypropane
2-ethoxypropane
3-methylpentan-3-ol will be prepared from
ethyl formate and methyl magnesium bromide
ethyl ethanoate and ethyl magnesium bromide
ethyl propanoate and methyl magnesium bromide
ethyl formate and ethyl magnesium bromide
