Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe region between two concentric spheres of radii ‘a’ and ‘b’, respectively (see figure), has volume charge density ρ = A/r , where A is a constant and r is the distance from the centre. At the centre of the spheres is a point charge Q. The value of A such that the electric field in the region between the spheres will be constant is: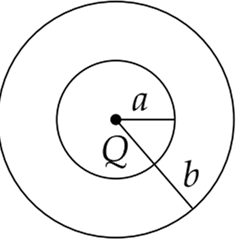

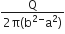
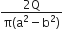
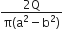
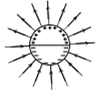
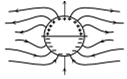
A long cylindrical shell carries positive surface charge in the upper half and negative surface charge in the lower half. The electric field lines around the cylinder will look like figure given in: (figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)


Two charges, each equal to q, are kept at x = −a and x = a on the x-axis. A particle of mass m and charge qo =-q/2 is placed at the origin. If charge qo is given a small displacement (y<< a) along the y-axis, the net force acting on the particle is proportional to
y
-y
1/y
1/y
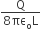
A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a long rod AB of length L as shown in the figure. The electric potential at the point O lying at a distance L from the end A is![]()
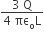


This question has statement 1 and statement 2. Of the four choices given after the statements, choose the one that best describes the two statements.
An insulating solid sphere of radius R has a uniformly positive charge density ρ. As a result of this uniform charge distribution, there is a finite value of the electric potential at the centre of the sphere, at the
surface of the sphere and also at a point out side the sphere. The electric potential at infinity is zero.
Statement 1: When a charge q is taken from the centre to the surface of the sphere, its potential energy changes by qρ/3εo
Statement 2: The electric field at a distance r(r < R) from the centre of the sphere is ρr/3εo
Statement 1 is true, Statement 2 is true, Statement 2 is not the correct explanation for statement 1.
Statement 1 is true, Statement 2 is false
Statement 1 is false, Statement 2 is true
Statement 1 is false, Statement 2 is true
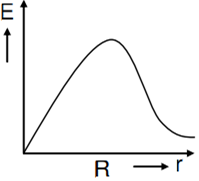
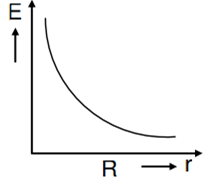
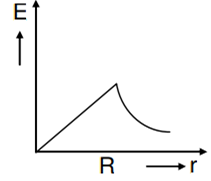
In a uniformly charged sphere of total charge Q and radius R, the electric field E is plotted as a function of distance from the centre. The graph which would correspond to the above will be

Let there be a spherically symmetric charge distribution with charge density varying as 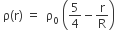 upto r = R, and ρ(r) = 0 for r > R, where r is the distance from the origin. The electric field at a distance r ( r < R) from the origin is given by
upto r = R, and ρ(r) = 0 for r > R, where r is the distance from the origin. The electric field at a distance r ( r < R) from the origin is given by
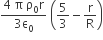
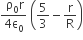
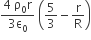
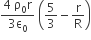
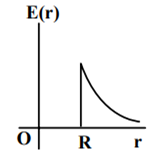
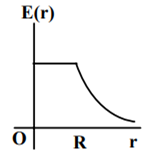
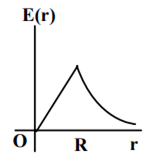
A thin spherical shell of radius R has charge Q spread uniformly over its surface. Which of the following graphs most closely represents the electric field E(r) produced by the shell in the range 0 ≤ r< ∞ , where r is the distance from the centre of the shell?

Charges are placed on the vertices of a square as shown. Let E be the electric field and V the potential at the centre. If the charges on A and B are interchanged with those on D and C respectively, then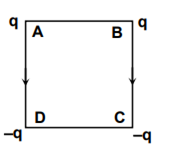
 remains unchanged, V changes
remains unchanged, V changes
Both  and V change
and V change
 and V remain unchanged
and V remain unchanged
 and V remain unchanged
and V remain unchanged
A charged particle with charge q enters a region of constant, uniform and mutually orthogonal fields  , with a velocity
, with a velocity  perpendicular to both
perpendicular to both  , and comes out without any change in magnitude or direction of
, and comes out without any change in magnitude or direction of  .Then
.Then