 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIf the magnitude of sum of two vectors is equal to the magnitude of difference of the two vectors, the angle between these vectors is,
90o
45o
180o
0o
Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two massless strings of lengths l, are initially at a distance d (d < l) apart because of their mutual repulsion. The charges begin to leak from both the spheres at a constant rate. As a result, the spheres approach each other with a velocity v. Then, v varies as a function of the distance x between the sphere, as
v![]() x
x
![]()
v![]() x-1
x-1
![]()
B.
![]()
Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two massless strings of length L.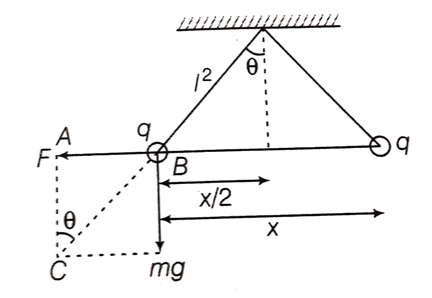
In △ABC,![]()
![]()
The charge begins to leak from both the sphere at a constant rate. As a result, the spheres approach each other with velocity v.
Therefore, equation (i) can be rewritten as,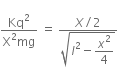
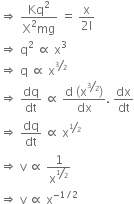
A ship A is moving Westwards with a speed of 10 kmh-1 and a ship B 100km south of A, is moving Northwards with a speed of 10 kmh-1. The time after which the distance between them becomes shortest is
0 h
5 h
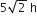
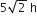
A particle is moving such that its position coordinates (x,y) are (2m, 3m) at time t = 0, (6m, 7m) at time t = 2 sec and (13 m, 14m) at time t= 5 sec. Average velocity vector (vav) from t = 0 to t = 5 s is,
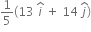
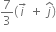
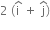
The force F acting on a particle of mass m is indicated by the force-time graph as shown below. The climate change in momentum of the particle over the time interval from zero to 8 s is,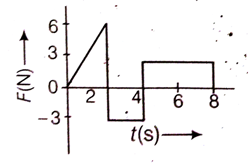
24 Ns
20 Ns
12 Ns
12 Ns
The motion of a particle along a straight line is described by equation
x=8+12 t -t3
where x is in metre and t in second. The retardation of the particle when its velocity becomes zero, is
24 ms-2
zero
6 ms-2
6 ms-2
A stone falls freely under gravity. It covers distances h1 , h2 and h3 in the first 5 seconds, the next 5 seconds and the next 5 seconds respectively. The relations between h1, h2 and h3 is,
h1 = 2 h2 = 3 h3
h1 = 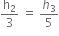
h2 = 3 h1 and h3 = 3 h2
h2 = 3 h1 and h3 = 3 h2
Three blocks will masses m, 2m and 3m are connected by strings, as shown in the figure. After an upward force F is applied on block m, the masses move upward at constant speed v. What is the net force on the block of mass 2m? (g is the acceleration due to gravity)
zero
2 mg
3 mg
3 mg
A uniform force of (3 i + j) N acts on a particle of mass 2 kg. Hence the particle is displaced from position (2 i + k) m to position ( 4 i + 3 j - k) m. The work done by the force on the particle is,
9 J
6 J
13 J
13 J
A plank with a box on it at one end is gradually raised about the other end. As the angle of inclination with the horizontal reaches 30o, the box starts to slip and slides 4.0 m down the plank in 4.0 s. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the box and the plank will be respectively
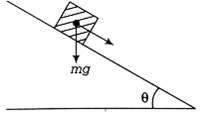
0.6 and 0.6
06 and 0.5
0.5 and 0.6
0.4 and 0.3
