 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn the following sequence of reactions,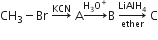
the end product is (C) is
acetone
methane
acetaldehyde
acetaldehyde
Which of the following reaction (s) can be used for the preparation of alkyl halides?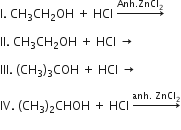
I, III and IV
I and II
Only IV
Only IV
In an SN1 reaction on chiral centres, there is
100% racemisation
inversion more than retention leading to partial racemization
100% retention
100% retention
The order of reactivity of phenyl magnesium bromide (phMgBr) with the following compounds.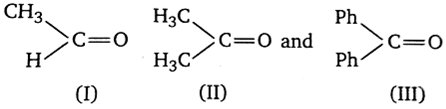
III > II> I
II > I > III
I > III > II
I > III > II
The IUPAC name of the following compound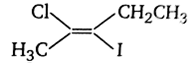
trans - 2- chloro - 3 - iodo - 2 - pentene
cis - 3- iodo - 4- chloro - 3- pentene
trans - 3- iodo - 4- chloro - 3- pentene
trans - 3- iodo - 4- chloro - 3- pentene
Consider the reactions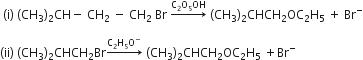
The mechanisms of reactions (i) and (ii) are respectively
SN1 and SN2
SN1 and SN1
SN2 and SN2
SN2 and SN2
In the reaction with HCl, an alkene reacts in accordance with the markownikoff's rule, to give a product 1-chloro -1- methylcyclohexane. The possible alkane is
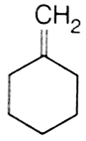
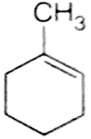
(a) and (b)
(a) and (b)
2,3 -dimethyl - 2- butene can be prepared by heating which of the following compounds with a strong acid?
(CH3)2CH-CH(CH)3-CH=CH2
(CH3)3C-CH=CH2
(CH3)2C =CH-CH2-CH3
(CH3)2C =CH-CH2-CH3
Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction?
C6H5CH(C6H5)Br
C6H5CH(CH3)Br
C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br
C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br
