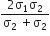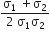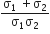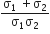Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA particle of unit mass and specific charge s is thrown from the wall perpendicularly to a wall at a distance d from the wall with speed 'v'. The minimum magnetic field produced so that the particle does not touch the wall, is:
A long straight wire of radius a carries a steady current I. The current is uniformly distributed over its cross-section. The ratio of the magnetic fields B and B' at radial distances 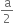 and 2a respectively, from the axis of the wire is,
and 2a respectively, from the axis of the wire is,
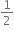
1
4
4
A magnetic needle suspended parallel to a magnetic field requires 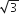 J of work to turn it through 60o. The torque needed to maintain the needle in this position will be
J of work to turn it through 60o. The torque needed to maintain the needle in this position will be
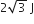
3 J


The ratio of amplitude of magnetic field to the amplitude of electric field for an electromagnetic wave propagating in vacuum is equal to
the speed of light in vacuum
the reciprocal of the speed of light in vacuum
the ratio of magnetic permeability to the electric susceptibility of vacuum
the ratio of magnetic permeability to the electric susceptibility of vacuum
Two similar coils of radius R are lying concentrically with their planes at right angles to each other. The currents flowing in them are I and 2I, respectively. The resultant magnetic field induction at the centre will be
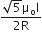
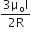
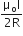
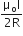
An electric dipole of moment p is placed in an electric field of intensity E. The dipole acquires a position such that the axis of the dipole makes an angle θ with the direction of the field. Assuming that the potential energy of the dipole to be zero when θ =90o, the torque and the potential energy of the dipole will respectively be
pE sin θ, pE cos θ
pE sin θ,-2pE cos θ
pE sin θ, 2 pE cos θ
pE sin θ, 2 pE cos θ
A wire loop is rotated in a magnetic field. The frequency of change of direction of the induced emf is
one per revolution
twice per revolution
four times per revolution
four times per revolution
The electric and the magnetic field, associated with an electromagnetic wave, propagating along the +z - axis, can be represented by
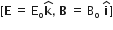



A proton and an alpha particle both enter a region of uniform magnetic field B, moving at angles to the field B. If the radius of circular orbits for both the particles is equal and the kinetic energy acquired by proton is 1 MeV, the energy acquired by the alpha particle will be
4 MeV
0.5 Mev
1.5 MeV
1.5 MeV
D.
1.5 MeV
Radius in magnetic field of circular orbit,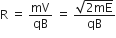
and total energy of a moving particle in a circular orbit,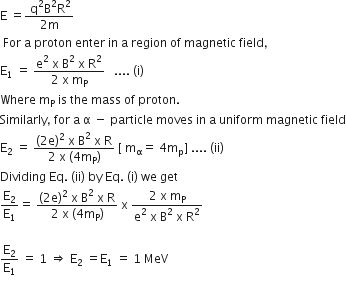
Two metal wires of identical dimensions are connected in series if σ1a nd σ2 are the conductivity of the metal wires respectively, the conductivity of the combination is