 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich type of DNA is found in bacteria
Helical DNA
Membrane bound DNA
Straight DNA
Circular free DNA
Refer to the given figure and select the correct option regarding its parts labelled as A, B and C.
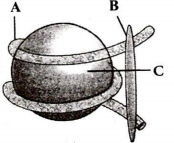
A-Histone octamer, C-DNA
B-H1 histone, C-Histone octamer
A-H1 histone, B-DNA
A-Histone octamer, C-H1 histone
Match the triplet codons listed in column I with their amino acids mentioned in column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
Column I Column II
A. GGG (i) Proline
B. UUU (ii) Glycine
C. CCC (iii) Arginine
D. AAA (iv) Phenylalanine
(v) Lysine
A-(v), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(ii)
A-(v), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(iv)
A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(v)
A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iii),D-(iv)
Radio-tracer technique shows that DNA is in
single-helix stage
double-helix stage
multi-helix stage
none of these
Assertion: The honeybee queen copulates only once in her life time.
Reason: The honeybee queen can lay fertilised as well as unfertilised eggs.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
In a 3.2 Kbp long piece of DNA, 820 adenine bases were found. What would be the number of cytosine bases?
780
1560
740
1480
Some of the steps of DNA fingerprinting are given below. Identify their correct sequence from the options given.
A. Electrophoresis of DNA fragments
B. Hybridisation with DNA probe
C. Digestion of DNA by restriction endonucleases
D. Autoradiography
E. Blotting of DNA fragmentsto nitrocellulose membrane
C - A - B - E - D
C - A - E - B - D
A - E - C - B - D
A - C - E - D - B
Which of the following set of options is used in translation
hnRNA, tRNA, rRNA
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
mRNA, tRNA, hnRNA
hnRNA, rRNA, tRNA
If the sequence of bases in the coding strand of a double stranded DNA is 5'-GTTCGAGTC-3', the sequence of bases in its transcript will be
5'-GACUCGAAC-3'
5'-CAAGCUCAG-3'
5'-GUUCGAGUC-3'
5'-CUGAGCUUG-3'
