CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Download this Mathematics Pre Board Paper 2 for taking the test offline or sharing with your friends. Once you are done with all the answers to the questions, Go ahead with answer key to check your answers.

General Instruction:

| 1. | Let A be the set of all students of a boys school. Show that the relation R in A given by R = {(a, b) : a is sister of b} is the empty relation and R’ = {(a, b) : the difference between heights of a and b is less than 3 meters} is the universal relation. | [1] |
| 2. |
Evaluates : | [1] |
| 3. |
If P1 , P2, P3, P4 are points in a plane or space and O, the origin of vectors, show that P4 coincides with O if an only if | [1] |
| 4. | Show that the function f : N → N given by f(x) = 2x, is one-one but not onto. | [1] |

| 5. |
Using principle value, evaluate the following : | [2] |
| 6. |
Construct a 3 x 4 matrix whose elements are ai j = i –J | [2] |
| 7. | Examine whether the function f given by f(x) = x2 is continuous at x = 0. | [2] |
| 8. |
The cost function C(x), in rupees, of producing x items (x ≥ 15) in a certain factory is given by | [2] |
| 9. |
Evaluate the following integral: | [2] |
| 10. |
Determine the order and degree of the differential equation: | [2] |
| 11. |
Find values of x for which | [2] |
| 12. |
Find the angle between the vector | [2] |

| 13. |
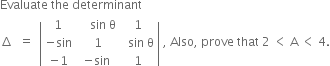
| [4] |
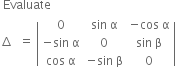
| 14. |
Discuss continuity of the function f given by f(x) = | x – 1| + | x – 2 ] at x = 1 and x = 2. | [4] |
| 15. |
The volume of a cube is increasing at a rate of 9 cubic centimeters per second. How fast is the surface area increasing when the length of an edge is 10 centimeters? | [4] |
| 16. |
Show that the following differential equation is homogeneous and find a primitive of it. Derive the solution wherever possible: | [4] |
Solve ![]()
| 17. |
Find all the points of discontinuity of the function f defined by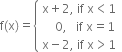
| [4] |
| 18. |
Evaluate | [4] |
| 19. |
If P, Q, R, S are the points (– 2, 3, 4), (– 4, 4, 6), (4, 3, 5), (0, 1, 2), prove by projection that PQ is perpendicular to RS. | [4] |
| 20. |
A die is thrown three times. Events A and B are defined as below: | [4] |
| 21. | A point source of light along a straight road is at a height of ‘a’ metres. A boy ‘b’ metres in height is walking along the road. How fast is his shadow increasing if he is walking away from the light at the rate of c metres per minute? | [4] |
| 22. |
ABCDEF is a regular hexagon. Show that (i) (ii) where O is centre of the hexagon. | [4] |
| 23. | An unbiased die is thrown twice. Let the event A be ‘odd number on the first throw’ and B the event ‘odd number on the second throw’. Check the independence of the events A and B. | [4] |

| 24. |
Show that each of the relation R in the set A = {x ∈ Z : 0 ≤ x ≤ 12 }, given by | [6] |
| 25. |
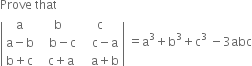
| [6] |
| 27. |
Evaluate: | [6] |
Draw a graph of ![]() and evaluate area bounded by it.
and evaluate area bounded by it.
| 28. |
A (– 1, 2, – 3), B (5, 0, – 6), C (0, 4, – 1) are three points. Show that the direction cosines of the bisectors of are proportional to 25, 8, 5 and -11, 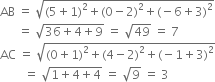
| [6] |
For the cartesian and vector equation of a line which passes through the point (1, 2, 3) and is parallel to the line ![]()
| 29. |
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically: Maximise Z = 4x + y subject to the constraints: x + y ≤ 50, 3x + y ≤ 90, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 | [6] |