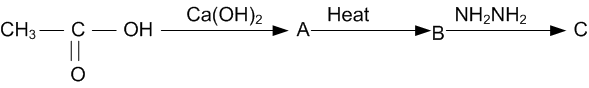CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Download this Chemistry Pre Board Paper 2 for taking the test offline or sharing with your friends. Once you are done with all the answers to the questions, Go ahead with answer key to check your answers.

General Instructions:

| 1. | What is the effect of pressure on NaCl type crystals? | [1] |
| 2. | What do you mean by adsorbent and adsorbate? | [1] |
| 3. | Why magnesium oxide is used for the lining in steel making furnance? | [1] |
| 4. | Write IUPAC name of the following: Tert-butyl chloride. | [1] |
| 5. |
Write the structure of compound A in the following reactions: | [1] |
| 6. | What is expected value of Van’t Hoff factor for K3 [Fe(CN)6] in dilute solution? | [2] |
| 7. | State any one condition under which a bimolecular reaction may be kinetically of first order? | [2] |
| 8. | Why reduction of a metal oxide becomes easier if the metal formed is in liquid state at the temperature of reduction? | [2] |
| 9. | Why does NO2 dimerise? | [2] |
| 10. |
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their acid strength. | [2] |
| 11. | Examine the illustration of a portion of the defective crystal given below and answer the following questions: (i) What are these types of vacancy defects called? (ii) How is the density of a crystal affected by these defects? (iii) Name one ionic compound which can show this type of defect in the crystalline state. (iv) How is the stoichiometry of the compound effected? 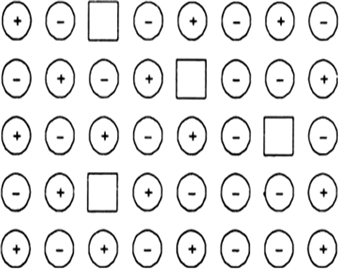 | [3] |
| 12. | The rate of reaction | [3] |
| 13. | Prove that the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to the mole fraction of non-volatile solute in the solution. | [3] |
| 14. | What is de-emulsification ? Name two demulsifiers. | [3] |
| 15. | A blackish brown coloured solid ‘A’, when fused with alkali hydroxide in presence of air produces a dark green coloured compound ‘B’. When electrolytic oxidation in alkaline medium gives a dark purple coloured compound. Identify A, B and C and write the reaction involved. | [3] |
| 16. | What do you understand by nucleophilic substitution reaction? Why do haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction? | [3] |
| 17. |
Give reasons: | [3] |
| 18. | A metal ion Mn+ having d4 valence electronic configuration combines with three didendate ligands to form complex compound. Assuming ∧0 > P. (i) Draw the diagram showing d-orbital splitting during this complex formation. (ii) Write the electronic configuration of the valence electrons of the metal Mn+ in terms to t2g, and eg . (iii) What type of hybridisation will Mn+ ion have? (iv) Name the type of isomerism exhibited by this complex. | [3] |
(i) Explain geometrical isomerism with reference to square planar complexes giving one example. How is tetrahedral complexes with simple ligands do not exhibit geometrical isomerism?
(ii) Using valence bond theory, predict the shape and magnetism (paramagnetism) or diamagnetism of [Co(CO)4]– (at. no. of Co = 27)?
(iii) How is stability of coordination compounds determined in aqueous solution?
| 19. |
Arrange the isomeric compounds: | [3] |
| 20. |
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers (i) Nylon-6, 6 (ii) PHBV (iii) Neoprene | [3] |
| 21. |
What are the following substances? Give one example of each. (i) Food preservatives (ii) Synthetic detergents (iii) Antacids | [3] |
| 22. |
(i) Write the IUPAC name of the complex [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Cl. | [3] |
| 23. |
After watching a programme on TV about the presence of carcinogens(cancer causing After reading the above passage, answer the following questions : | [4] |
| 24. | Depict the galvanic cell in which the reaction | [5] |
Give the product of the reaction of: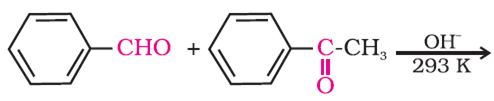
Predict the organic products of the following:
Predict the organic products of the following: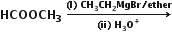
How will you make the following conversions?
Benzoic acid into 2-phenyl propan-2-ol.
How will you make the following conversions?
Ethyl acetate into but-2-enal.