CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Download this Chemistry Pre Board Paper 3 for taking the test offline or sharing with your friends. Once you are done with all the answers to the questions, Go ahead with answer key to check your answers.

General Instructions:

| 1. | What makes the crystal of KCl appear sometimes violet? | [1] |
| 2. | What is desorption? | [1] |
| 3. | Which method of metal refining is generally used when a metal of high degree of purity is needed? | [1] |
| 4. | Why is chloroform kept in dark bottles? | [1] |
| 5. |
Write IUPAC name of the following compounds: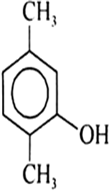 | [1] |
| 6. | Define Henry's law about solubility of a gas in a liquid. | [2] |
| 7. | Express the rate of reaction in terms of concentration of reactants and products for the reaction. | [2] |
| 8. | Predict the modes of occurrence of the following three types of metals: | [2] |
| 9. | In what why it can be proved that PH3 is basic in nature? | [2] |
| 10. |
Give reason: nitration of phenol gives ortho and para products only. | [2] |
| 11. | Iron (II) oxide has a cubic structure and each unit cell has side 5A. If the density of the oxide is 4 g cm–3, calculate the number of Fe2+ and O2– ions present in each unit cell. (Molar mass of FeO = 72 g mol–1, NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol–1). | [3] |
| 12. | (a)Show graphically how the rate of a first order reaction with only one reactant depends upon the concentration of the reactant. (b) Give one example of a first order reaction. | [3] |
| 13. | Give one example each of miscible liquid pairs showing positive and negative deviatins from Raoult’s law. Give one reason for such deviations. | [3] |
| 14. | Explain the following terms with an example of each: | [3] |
| 15. | How would you account for the following situations? With 3d4 configuration, Cr2+ acts as a reducing agent but Mn3+ acts as an oxidising agent. (Atomic masses, Cr = 24, Mn = 25). | [3] |
| 16. | Although chlorine is an electron-withdrawing group, yet it is ortho, para-directing in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Why? | [3] |
| 17. |
Explain each of the following observations: (i) With the same d-orbital configuration (d4), Cr2+ is a reducing agent while Mn3+ is an oxidising agent. (ii) Actinoids exhibit a much larger number of oxidation states than the lanthanoids. (iii) There is hardly any increase in atomic size with increasing atomic number in a series of transition metals. | [3] |
| 18. | [Fe(CN)6]4– is diamagnetic while [FeF6]4– is strongly paramagnetic. Why? | [3] |
Deduce the structures of [NiCl4]2– and [Ni(CN)4]2– considering the hybridization of the metal ion. Calculate the magnetic moment (spin only) of the species.
| 19. | A compound (X) having molecular formula C3H7NO, reacts with bromine and caustic soda to give another compound (Y). The compound (Y) reacts with HNO2 to form alcohol and nitrogen gas. Identify the compounds (X) and (Y) and write the chemical equations of the reactions involved. | [3] |
| 20. |
i) Write the structural difference between starch and cellulose. | [3] |
| 21. |
What are the following substances? Give one example of each one of them. (i) Tranquilizers (ii) Food preservatives (iii) Synthetic detergents | [3] |
| 22. |
Write the state of hybridization, the shape and the magnetic behaviour of the following complex entities: (i) [Cr (NH3)4 Cl2] Cl (ii) [Co (en) 3] Cl3 (iii) K2 [Ni (CN) 4] | [3] |
| 23. |
After the ban on plastic bags, students of a school decided to make people aware of the harmful effects of plastic bags on the environment and Yamuna River. To make the awareness more impactful, they organised a rally by partnering with other schools and distributed paper bags to vegetable vendors, shopkeepers and departmental stores. All the students pledged not to use polythene bags in the future to save the Yamuna River. After reading the above passage, answer the following questions: <(i) What values are shown by the students? (ii) What are bio-degradable polymers? Give one example. (iii) Is polythene a condensation or an addition polymer ? | [4] |
The following curve is obtained when molar conductivity λm (y-axis) is plotted against the square root of concentration C1/2 (x-axis) for two electrolytes A and B.
(a) What can you about the nature of the two electrolytes A and B.
(b) How do you account for the increase in molar conductivity λm for the electrolytes A and B on dilution.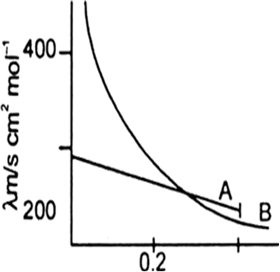
Explain the mechanism of aldol condensation using ethanal as an example.
Account for the following:
Carboxylic acids with five or less carbons are water soluble, but many with six or more carbons dissolves in alcohols.
