CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Download this Chemistry Pre Board Paper 4 for taking the test offline or sharing with your friends. Once you are done with all the answers to the questions, Go ahead with answer key to check your answers.

General Instructions:

| 1. | What is the maximum possible coordination number of an atom in an hcp crystal structure of an element? | [1] |
| 2. | What do you mean by sorption? | [1] |
| 3. | How does NaCN act as a depressant in preventive ZnS from forming the froth? | [1] |
| 4. |
What happens when CH3CH2Cl is boiled with alcholoic KOH? | [1] |
| 5. |
Write IUPAC name of: CH3O—CH2—CH—OCH3 | [1] |
| 6. | When is value of Van’t Hoff factor more than one? | [2] |
| 7. | What is the rate and order of a reaction of the mechanism is Following by (fast) | [2] |
| 8. | Write the chemical reactions involved in the extraction of metallic silver from argentite. | [2] |
| 9. | Are all the five bonds in PCl5 molecule equivalent? Justify your answer. | [2] |
| 10. |
What is the expected product from the reaction of with (i) LiAlH4, (ii) H2/Pt? | [2] |
| 11. | An element E crystallizes in body centred cubic structure. If the edge length of the cell is 1.469 x 10–10 m and the density is 19.3 g cm–3, calculate the atomic mass of this element. Also calculate the radius of this element. | [3] |
| 12. | A possible mechanism for the reaction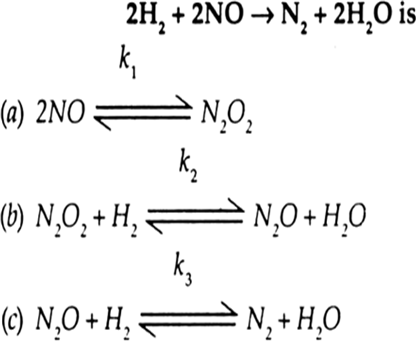 If the second step is the rate determining step, what is the rate law for this reaction? | [3] |
| 13. | How does osmotic pressure depend on molality of the solution? | [3] |
| 14. | A colloidal solution of Agl is prepared by two different methods shown below: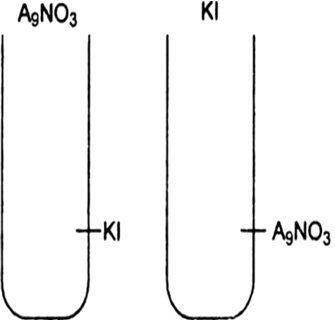 (i) What is the charge of AgI colloidal particles in the two test tube (A) and (B). | [3] |
| 15. | Describe the general characteristics of the transition elements with special reference to their tendency to: | [3] |
| 16. |
A hydocarbon (Z) has molecular formula C8H10. It does not decolourise bromine water and is oxidised to benzoic acid on heating with K2Cr2O7 . It can also have the three other isomers A, B and C. Write the structure of A, B and C. | [3] |
| 17. |
Complete the following chemical equations: | [3] |
Using IUPAC norms write the formulate for the following coordination compounds:
(i) Hexaamminecobalt (III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetrachloridonickelate (II)
On adding NaOH to ammonium sulphate, a colourless gas with pungent odour is evolved, which forms a blue-coloured complex with Cu2+ ion. Identify the gas.
What is meant by crystal field splitting energy? On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of d4 in terms of t2g and eg in an octahedral field when
(i)![]() 0 > P
0 > P
(ii) ![]() 0 < P
0 < P
| 19. | A substance (X) has a molecular formula C3H9N. This substance gives a unpleasant smell with chloroform and caustic potash. Write the structure of this organic substances (X). Write their IUPAC names also. | [3] |
| 20. |
Comment on: | [3] |
| 21. |
Describe the following with suitable examples: | [3] |
| 22. |
(a) For the complex [Fe(CN)6]3–, write the hybridization type, magnetic character and spin nature of the complex. (At. number : Fe = 26). | [3] |
| 23. |
Shanti, a domestic helper of Mrs. Anuradha, fainted while mopping the floor. Mrs. Anuradha immediately took her to the nearby hospital where she was diagnosed to be severely ‘anaemic’. The doctor prescribed an iron rich diet and multivitamins supplement to her. Mrs. Anuradha supported her financially to get the medicines. After a month, Shanti was diagnosed to be normal. (i) What values are displayed by Mrs. Anuradha? (ii) Name the vitamin whose deficiency causes ‘pernicious anaemia’. (iii) Give an example of a water soluble vitamin. | [4] |
| 24. | Three electrolytic cells A, B and C containing solutions of ZnSO4(zinc sulphate), AgNO3 (silver nitrate) and CuSO4 (copper sulphate), respectively are connected in series. A steady current of 1.5 ampere was passed through them until 1.45 g of silver is deposited at the cathode of cell B. How long did the current flow? What mass of copper and zinc were deposited? (Atomic masses: Ag = 108, Zn = 65.4, Cu = 63.5, all in amu). | [5] |
| 25. | Give reasons for: (i) Ozone is more reactive than oxygen. (ii) An acidified K2Cr2O7 paper on being exposed to SO2 turns green. (iii) Sulphuric acid never acts as a reducing agent. (iv) Noble gases are mostly chemically inert. (v) Nitrogen is fairly inert. | [5] |
What is the basicity of H3PO4?
Account for the following:
(i) Chloroacetic acid has higher pKa value than acetic acid.
(ii) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta position.
(iii) Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
discuss hell -vollhard -zelinsky reaction (HVZ) ?
Discuss Rosenmud's reaction.