CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Download this Physics Pre Board Paper 1 for taking the test offline or sharing with your friends. Once you are done with all the answers to the questions, Go ahead with answer key to check your answers.

General Instructions:
There is no overall choice. However, an Internal Choice has been provided in one question of Two Marks, one question of Three Marks and all the Three Questions of Five Marksweightage. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such Questions.

| 1. |
Two charges of magnitudes – 2Q and + Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘3a’ with its centre at the origin? | [1] |
| 2. |
When electrons drift in a metal from lower to higher potential, does it mean that all the free electrons of the metal are moving in the same direction? | [1] |
| 3. | A concave lens of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in a medium of refractive index 1.65. What is the nature of the lens ? | [1] |
| 4. |
Two identical cells, each of emf E, having negligible internal resistance, are connected in parallel with each other across an external resistance R. What is the current through this resistance? | [1] |
| 5. |
What is the function of a 'Repeater' used in communication system? | [1] |

| 6. |
A slab of material of dielectric constant K has the same area as that of the plates of a parallel plate capacitor but has the thickness d/2, where d is the separation between the plates. Find out the expression for its capacitance when the slab is inserted between the plates of the capacitor. | [2] |
| 7. | A proton and an α-particle have the same de-Broglie wavelength. Determine the ratio of (i) their accelerating potentials (ii) their speeds. | [2] |
| 8. |
Define ionisation energy. | [2] |
Using the curve for the binding energy per nucleon as a function of mass number A, state clearly how the release in energy in the processes of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion can be explained.
| 9. |
In the block diagram of a simple modulator for obtaining an AM signal, shown in the figure, identify the boxes A and B. Write their functions. | [2] |
| 10. | Find an expression for intensity of transmitted light when a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids. In which position of the polaroid sheet will the transmitted intensity be maximum? | [2] |

| 11. |
Using Gauss's law obtains the expression for the electric field due to a uniformly charged thin spherical shell of radius R at a point outside the shell. Draw a graph showing the variation of electric field with r, for r > R and r < R. | [3] |
| 12. |
A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance ‘r’ is connected across a variable load resistor R. Draw the plots of the terminal voltage V versus | [3] |
| 13. |
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is (a) suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. (b) used to treat muscular strain. (c) used as a diagnostic tool in medicine. Write in brief, how these waves can be produced. | [3] |
| 14. |
Two capacitors of unknown capacitances C1 and C2 are connected first in series and then in parallel across a battery of 100 V. If the energy stored in the two combinations is 0.045 J and 0.25 J respectively, determine the value of C1 and C2. Also, calculate the charge on each capacitor in parallel combination. | [3] |
| 15. |
(a) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the formation of a final image by a compound microscope at least distance of distinct vision. (b) The total magnification produced by a compound microscope is 20. The magnification produced by the eye piece is 5. The microscope is focused on a certain object. The distance between the objective and eyepiece is observed to be 14 cm. If least distance of distinct vision is 20 cm, calculate the focal length of the objective and the eye piece. | [3] |
| 16. |
Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation and point out any two characteristic properties of photons on which this equation is based. Briefly explain the three observed features which can be explained by this equation. | [3] |
| 17. |
A wire AB is carrying a steady current of 12 A and is lying on the table. Another wire CD carrying 5A is held directly above AB at a height of 1 mm. Find the mass per unit length of the wire CD so that it remains suspended at its position when left free. Give the direction of the current flowing in CD with respect to that in AB. | [3] |
| 18. |
(a) What is linearly polarized light? Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised. (b) Unpolarized light is incident on a Polaroid. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
| [3] |
| 19. |
A 12.5 eV electron beam is used to bombard gaseous hydrogen at room temperature. Upto which energy levels the hydrogen atoms would be excited? Calculate the wavelengths of the first member of Lyman and first member of Balmer series. | [3] |
| 20. |
For a CE-transistor amplifier, the audio signal voltage across the collector resistance of 2 kΩ is 2 V. Given the current amplification factor of the transistor is 100, find the input signal voltage and base current, if the base resistance is 1 kΩ. | [3] |
| 21. | Communication in UHF/VHF regions can be established by space or tropospheric wave. Why is it restricted to or limited to line-of-sight distance of about 40 km? | [3] |
| 22. |
Draw V – I characteristics of a p–n junction diode. Answer the following questions, giving reasons: (i) Why is the current under reverse bias almost independent of the applied potential up to a critical voltage? (ii) Why does the reverse current show a sudden increase at the critical voltage? Name any semiconductor device which operates under the reverse bias in the breakdown region. | [3] |

| 23. |
Ram is a student of class X in a village school. His uncle gifted him a bicycle with a dynamo fitted in it. He was very excited to get it. While cycling during night, he could light the bulb and see the objects on the road. He, however, did not know how this device works. He asked this question to his teacher. The teacher considered it an opportunity to explain the working to the whole class. | [4] |

| 24. |
(a) Deduce the expression for the torque acting on a dipole of dipole moment p in the presence of a uniform electric field E⃗. (b) Consider two hollow concentric spheres, S1 and S2, enclosing charges 2Q and 4Q respectively as shown in the figure. (i) Find out the ratio of the electric flux through them. (ii) How will the electric flux through the sphere S1 change if a medium of dielectric constant 'εr' is introduced in the space inside S1 in place of air ? Deduce the necessary expression.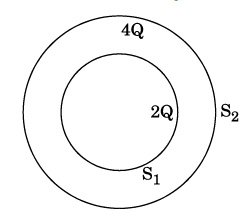
| [5] |
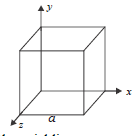
(a) An electric dipole of dipole moment p⃗ consists of point charges +q and –q separated by a distance 2a apart. Deduce the expression for the electric field E⃗ due to the dipole at a distance x from the center of the dipole on its axial line in terms of the dipole moment p⃗. Hence show that in the limit x >> a, E⃗ → 2 p⃗/ (4p ε0 x3).
(b) Given the electric field in the region E⃗ = 2x i, find the net electric flux through the cube and the charge enclosed by it.
| 25. |
Draw a necessary arrangement for winding of primary and secondary coils in a step-up transformer. State its underlying principle and derive the relation between the primary and secondary voltages in terms of number of primary and secondary turns. Mention the two basic assumptions used in obtaining the above relation. State any two causes of energy loss in actual transformers. | [5] |
Derive an expression for the impedance of a series LCR circuit connected to an AC supply of variable frequency.
Plot a graph showing variation of current with the frequency of the applied voltage.
Explain briefly how the phenomenon of resonance in the circuit can be used in the
Tuning mechanism of a radio or a TV set.| 26. |
(a) Obtain lens makers formula using the expression Here the ray of light propagating from a rarer medium of refractive index (n1) to a denser medium of refractive index (n2) is incident on the convex side of spherical refracting surface of radius of curvature R. (b) Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation by a concave mirror when the object is kept between its focus and the pole. Using this diagram, derive the magnification formula for the image formed. | [5] |
(a) Using Huygens’s construction of secondary wavelets explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a monochromatic beam of light is incident normally.
(b) Show that the angular width of the first diffraction fringe is half that of the central fringe.
(c) Explain why the maxima at 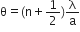 become weaker and weaker with increasing n.
become weaker and weaker with increasing n.