CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Download this Physics Pre Board Paper 2 for taking the test offline or sharing with your friends. Once you are done with all the answers to the questions, Go ahead with answer key to check your answers.

General Instructions:
There is no overall choice. However, an Internal Choice has been provided in one question of Two Marks, one question of Three Marks and all the Three Questions of Five Marksweightage. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such Questions.

| 1. | Define the term ‘potential energy’ of charge ‘q’ at a distance ‘r’ in an external electric field. | [1] |
| 2. |
Two identical cells, each of emf E, having negligible internal resistance, are connected in parallel with each other across an external resistance R. What is the current through this resistance? | [1] |
| 3. |
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force | [1] |
| 4. |
For the same value of angle incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum? | [1] |
| 5. |
The figure given below shows the block diagram of a generalized communication system. Identify the element labelled 'X' and write its function. | [1] |

| 6. | Write an expression for the resistivity of a metallic conductor showing its variation over a limited range of temperatures. | [2] |
| 7. | Ultraviolet light is incident on two photosensitive materials having work functions W1 and W2 (W1 > W2). In which case will the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons be greater? Why? | [2] |
| 8. |
Show that the radius of the orbit in hydrogen atom varies as , where n is the principal quantum number of the atom. | [2] |
| 9. | A nucleus nXm emits one alpha particle and one beta particle. Find the mass number and atomic number of the product nucleus. | [2] |
| 10. | How does the power of a convex lens vary, if the incident red light replaced by violet light? | [2] |

| 11. | The electric field E due to a point charge at any point near it is defined as where q is the test charge and F is the force acting on it. What is the physical significance of in this expression? Draw the electric field lines of a point charge Q when (i) Q > 0 and (ii) Q < 0 | [3] |
| 12. |
A potentiometer wire of length 1 m has a resistance of 10 Ω. It is connected to a 6 V battery in series with a resistance of 5 Ω. Determine the emf of the primary cell which gives a balance point at 40 cm. | [3] |
| 13. |
(a) State Ampere's circuital law, expressing it in the integral form. (b) Two long coaxial insulated solenoids, S1 and S2 of equal lengths are wound one over the other as shown in the figure. A steady current 'I' flow thought the inner solenoid S1 to the other end B, which is connected to the outer solenoid S2 through which the same current 'I' flows in the opposite direction so as to come out at end A. If n1 and n2 are the number of turns per unit length, find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at a point (i) Inside on the axis, and(ii) outside the combined system. 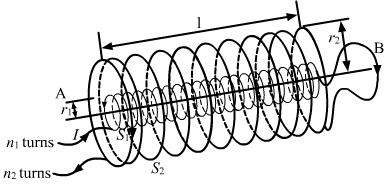
| [3] |
| 14. | Which of the following, if any, can act as a source of electromagnetic waves? 1. A charge moving with a constant velocity. 2. A charge moving in a circular orbit. 3. A charge at rest. Give reason. Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to which waves of frequency (i) 1020 Hz, (ii) 10P Hz belong. Find the ratio of their velocities in glass (n = 1.5). | [3] |
| 15. |
A circular coil of N turns and radius R carries a current I. It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of radius R/2, current I remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic moments of the new coil and the original coil. | [3] |
| 16. |
Draw a labelled ray diagram of a refracting telescope. Define its magnifying power and write the expression for it. Write two important limitations of a refracting telescope over a reflecting type telescope. | [3] |
| 17. |
Sketch the graphs showing variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiations for two photosensitive materials A and B having threshold frequencies | [3] |
| 18. |
(a) What is linearly polarized light? Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised. (b) Unpolarized light is incident on a Polaroid. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
| [3] |
| 19. |
(a) Using Bohr’s second postulate of quantization of orbital angular momentum show that the circumference of the electron in the nth orbital state in hydrogen atom is n times the de Broglie wavelength associated with it. (b) The electron in hydrogen atom is initially in the third excited state. What is the maximum number of spectral lines which can be emitted when it finally moves to the ground state? | [3] |
| 20. |
You are given a circuit below. Write its truth table. Hence, identify the logic operation carried out by this circuit. Draw the logic symbol of the gate it corresponds to. | [3] |
| 21. |
Write three important factors which justify the need of modulating a message signal. Show diagrammatically how an amplitude modulate wave is obtained when a modulating signal is superimposed on a carrier wave. | [3] |
| 22. |
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a p-n junction. | [3] |

| 23. |
A group of students while coming from the school noticed a box marked “Danger H.T. 2200 V” at a substation in the main street. They did not understand the utility of such a high voltage, while they argued; the supply was only 220 V. They asked their teacher this question the next day. The teacher thought it to be an important question and therefore explained to the whole class. Answer the following questions: (i) What device is used to bring the high voltage down to low voltage of a.c. current and what is the principle of its working? (ii) Is it possible to use this device for bringing down the high dc voltage to the low voltage? Explain. iii) Write the values displayed by the students and the teacher. | [4] |

| 24. |
(a) Define electric dipole moment. Is it a scalar or a vector? Derive the expression for the electric field of a dipole at a point on the equatorial plane of the dipole. (b) Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. Locate the points where the potential due to the dipole is zero. | [5] |
| 25. |
(i) With the help of a labelled diagram, describe briefly the underlying principle and working of a step up transformer. (ii) Write any two sources of energy loss in a transformer. (iii) A step up transformer converts a low input voltage into a high output voltage. Does it violate law of conservation of energy? Explain. | [5] |
A metallic rod of length ‘l’ is rotated with a frequency v with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius r, about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant uniform magnetic field B parallel to the axis is present everywhere. Using Lorentz force, explain how emf is induced between the centre and the metallic ring and hence obtain the expression for it.
| 26. |
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show refraction of a ray of monochromatic light passing through a glass prism. Deduce the expression for the refractive index of glass in terms of angle of prism and angle of minimum deviation. (b) Explain briefly how the phenomenon of total internal reflection is used in fiber optics. | [5] |
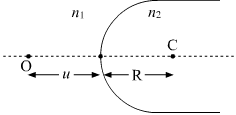
A point object 'O' is kept in a medium of refractive index n1 in front of a convex spherical surface of radius of curvature R which separates the second medium of refractive index n2 from the first one, as shown in the figure.
Draw the ray diagram showing the image formation and deduce the relationship between the object distance and the image distance in terms of n1, n2 and R.