 Short Answer Type
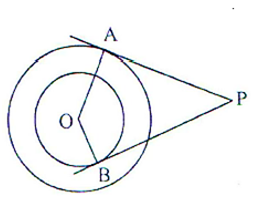
Short Answer TypeTangents PA and PB are drawn from an external point P to two concentric circle with centre O and radii 8 cm and 5 cm respectively, as shown in Fig., If AP = 15 cm, then find the length of BP.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIn fig., an isosceles triangle ABC, with AB =AB, circumscribes a circle. Prove that the point of contact P bisects the base BC.

OR
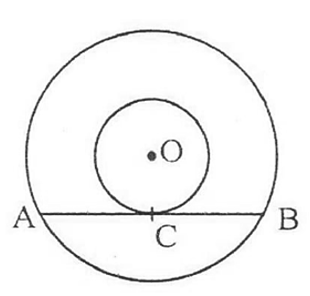
In fig., the chord AB of the larger of the two concentric circles, with centre O, touches the smaller circle at C. Prove that AC = CB.
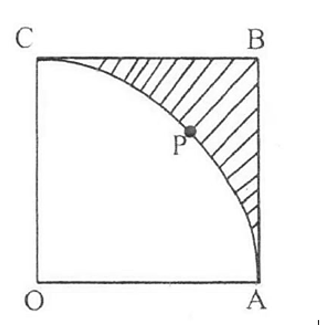
In fig., OABC is a square of side 7 cm. If OAPC is a quadrant of a circle with centre O, then find the area of the shaded region.
A point P divides the line segment joining the points A(3,-5) and B(-4, 8) such that . If P lies on the line x + y = 0, then find the value of K.
If the vertices of a triangle are (1, -3), (4, p) and (-9, 7) and its area is 15 sq. units, find the value (s) of p.
Prove that the parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus.
OR
Prove that opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.
From a solid cylinder of height 7 cm and base diameter 12 cm, a conical cavity of same height and same base diameter is hollowed out. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid.
OR
A cylindrical bucket, 32 cm high and with radius of base 18 cm, is filled with sand. This bucket is emptied on the ground and a conical heap of sand is formed. If the height of the conical heap is 24 cm, then find the radius and slant height of the heap.

Given: Radius of cylinder = radius of cone = r = 6 cm.
Height of the cylinder = height of the cone = h = 7 cm.
Slant height of the cone = l cm.
Total surface area of the remaining solid = curved surface area of the
cylinder + area of the base of the cylinder + curved surface area of the cone.
OR
Volume if the conical heap = volume of the sand emptied from the bucket.
Volume of the conical heap =
= .....(Height of the conies 24cm)
...........(1)
Volume of the sand in the bucket =
Equating (1) and (2)
