 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain how equal genetic contribution of male and female parents is ensured in the progeny.
Out of HCl and CH3COOH, which one is a weak acid and why? Describe an activity to support your answer.
Two elements X and Y belong to group 1 and 2 respectively in the same period of the periodic table. Compare them with respect to:
(i) the number of valences electrons in their atoms
(ii) their valencies
(iii) metallic character
(iv) the sizes of their atoms
(v) the formulae of their oxides
(vi) the formulae of their chlorides
Draw the ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
(i) “The refractive index of diamond is 2.42”. What is the meaning of this statement?
(ii) Name a liquid whose mass density is less than that of water but it is optically denser than water.
What eye defect is hypermetropia? Describe with a ray diagram how this defect of vision can be corrected by using an appropriate lens.
(a) List two sexually transmitted disease in each of the following cases:
(i) Bacterial infections
(ii) Viral infections
(b) How may the spread of such diseases be prevented?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) If the image formed by a lens is diminished in size and erect, for all positions of the object, what type of lens is it?
(b) Name the point on the lens through which a ray of light passes undeviated.
(c) An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find (i) the position (ii) the magnification and (iii) the nature of the image formed.
(a) If the image formed by a lens is diminished in size and erect, for all positions of the object, then the lens is a concave lens.
(b) The point on the lens through which a ray of light passes undeviating is known as Pole.
(c) Given,
Object distance, u = -30 cm
Focal length, f =20 cm
i) Now, using the len’s formula,
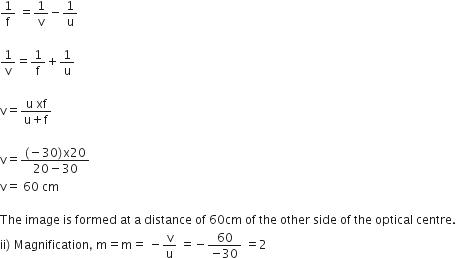
(iii) Image formed is inverted.
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will such a lens produce an image of the complete object? Support your answer with a ray diagram.
(b) An object 5 cm high is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm.
(i) Draw the ray diagram and
(ii) Calculate the position and size of the image formed.
(iii) What is the nature of the image?
